PRO: Persistent Central Sleep Apnea/Hunter-Cheyne-Stokes Breathing, Despite Best Guideline-Based Therapy of Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction, Is a Compensatory Mechanism and Should Not Be Suppressed
- PMID: 29860966
- PMCID: PMC5991963
- DOI: 10.5664/jcsm.7146
PRO: Persistent Central Sleep Apnea/Hunter-Cheyne-Stokes Breathing, Despite Best Guideline-Based Therapy of Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction, Is a Compensatory Mechanism and Should Not Be Suppressed
Figures
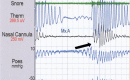
Comment in
-
Rebuttal to Naughton.J Clin Sleep Med. 2018 Jun 15;14(6):923-925. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.7150. J Clin Sleep Med. 2018. PMID: 29852919 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Naughton MT, Kee K. Sleep apnoea in heart failure: to treat or not to treat? Respirology. 2017;22(2):217–229. - PubMed
-
- Solin P, Snell GI, Williams TJ, Naughton MT. Central sleep apnoea in congestive heart failure despite vagal denervation after bilateral lung transplantation. Eur Respir J. 1998;12(2):495–498. - PubMed
-
- Mansfield D, Kaye DM, Brunner La Rocca H, Solin P, Esler MD, Naughton MT. Raised sympathetic nerve activity in heart failure and central sleep apnea is due to heart failure severity. Circulation. 2003;107(10):1396–1400. - PubMed
-
- Sun SY, Wang W, Zucker IH, Schultz HD. Enhanced activity of carotid body chemoreceptors in rabbits with heart failure: role of nitric oxide. J Appl Physiol. 1999;86(4):1273–1282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

