Protein Lipidation in Cell Signaling and Diseases: Function, Regulation, and Therapeutic Opportunities
- PMID: 29861273
- PMCID: PMC6054547
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2018.05.003
Protein Lipidation in Cell Signaling and Diseases: Function, Regulation, and Therapeutic Opportunities
Abstract
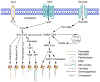
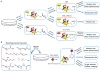
Protein lipidation is an important co- or posttranslational modification in which lipid moieties are covalently attached to proteins. Lipidation markedly increases the hydrophobicity of proteins, resulting in changes to their conformation, stability, membrane association, localization, trafficking, and binding affinity to their co-factors. Various lipids and lipid metabolites serve as protein lipidation moieties. The intracellular concentrations of these lipids and their derivatives are tightly regulated by cellular metabolism. Therefore, protein lipidation links the output of cellular metabolism to the regulation of protein function. Importantly, deregulation of protein lipidation has been linked to various diseases, including neurological disorders, metabolic diseases, and cancers. In this review, we highlight recent progress in our understanding of protein lipidation, in particular, S-palmitoylation and lysine fatty acylation, and we describe the importance of these modifications for protein regulation, cell signaling, and diseases. We further highlight opportunities and new strategies for targeting protein lipidation for therapeutic applications.
Keywords: bioorthogonal chemical reporters; cancer; drug discovery; fatty acylation; infectious diseases; palmitoylation; protein lipidation; signal transduction.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Adlanmerini M, Solinhac R, Abot A, Fabre A, Raymond-Letron I, Guihot AL, Boudou F, Sautier L, Vessieres E, Kim SH, et al. Mutation of the palmitoylation site of estrogen receptor alpha in vivo reveals tissue-specific roles for membrane versus nuclear actions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:E283–290. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alvarez R, Lopez DJ, Casas J, Llado V, Higuera M, Nagy T, Barcelo M, Busquets X, Escriba PV. G protein-membrane interactions I: Galphai1 myristoyl and palmitoyl modifications in protein-lipid interactions and its implications in membrane microdomain localization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1851:1511–1520. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

