Hemostatic Abnormalities in Severe Renal Failure: Do They Bark or Bite?
- PMID: 29861564
- PMCID: PMC5952452
- DOI: 10.4103/ijn.IJN_104_17
Hemostatic Abnormalities in Severe Renal Failure: Do They Bark or Bite?
Abstract
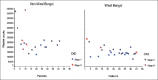
Abnormal primary hemostasis is believed to be the most significant contributor to uremic bleeding. This study aimed to describe the prevalence and profile of primary and secondary hemostatic disorders in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) Stages 4 and 5 and to determine their association if any, with degree of uremia. Stages 4 and 5 predialysis CKD patients attending nephrology outpatient clinic were prospectively recruited and the following bleeding parameters were measured in all patients: platelet count, bleeding time (BT), Factor VIII assay, von Willebrand factor antigen (vWF:Ag), vWF:ristocetin cofactor activity (vWF:RCo), ratio of vWF:ristocetin cofactor activity to vWF antigen (vWF:RCo/vWF:Ag), prothrombin time (PT), and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT). Forty-five patients (80%, males) with a mean age of 39.4 years, 82% (n = 37) in Stage 5 CKD, were recruited for the study. The prevalence of thrombocytopenia was significantly higher among patients from West Bengal (15/26, 57.7%) compared to other study patients (2/19, 10.5%; P = 0.001); however, all had macrothrombocytes with normal BT, suggestive of the Harris syndrome. Factor VIII, vWF:Ag, vWF:RCo, vWF:RCo/vWF:Ag ratio, BT, PT, and aPTT were abnormal in 0 (0%), 0 (0%), 0 (0%), 4 (8.8%), 1 (2.2%), 7 (15.6%), and 5 (11.1%) patients, respectively. Except for thrombocytopenia, the prevalence of hemostatic abnormalities did not differ between CKD Stages 4 and 5. Hemostatic abnormalities are uncommon in Stages 4-5 CKD and except for thrombocytopenia, are not associated with degree of uremia. Constitutional macrothrombocytopenia is associated with normal BT even in CKD.
Keywords: Bleeding time; Harris syndrome; chronic kidney disease; hemostasis; macrothrombocytopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Boccardo P, Remuzzi G, Galbusera M. Platelet dysfunction in renal failure. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2004;30:579–89. - PubMed
-
- Shetty HG, Almeida A, Sheth SM, Chawla KP, Acharya VN. Coagulation studies in uraemia. J Postgrad Med. 1982;28:149–59. - PubMed
-
- Varughese S, John GT, Alexander S, Deborah MN, Nithya N, Ahamed I, et al. Pre-tertiary hospital care of patients with chronic kidney disease in India. Indian J Med Res. 2007;126:28–33. - PubMed
-
- Michalak E, Walkowiak B, Paradowski M, Cierniewski CS. The decreased circulating platelet mass and its relation to bleeding time in chronic renal failure. Thromb Haemost. 1991;65:11–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

