Ceftriaxone and clavulanic acid induce antiallodynia and anti-inflammatory effects in rats using the carrageenan model
- PMID: 29861639
- PMCID: PMC5968784
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S154661
Ceftriaxone and clavulanic acid induce antiallodynia and anti-inflammatory effects in rats using the carrageenan model
Abstract
Introduction: Ceftriaxone (CFX) and clavulanic acid (CA) are 2 β-lactam molecules widely used as antibiotics. However, several reports of their antiallodynic properties have been published in recent years. Although this effect has been considered mostly due to a GLT1 overexpression, these molecules have also been proven to induce direct immunomodulation. In this work, we determine the acute analgesic effect of CFX and CA in an inflammatory pain model and assess if their administration may induce anti-inflammatory effects.
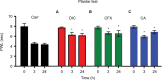
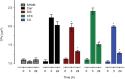
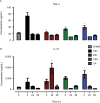
Methods: The carrageenan (Carr) test was used as an inflammatory pain model. Both mechanical and thermal responses were analyzed after CFX and CA administration at different times. A plethysmometer was used to determine inflammation. Also, TNF-α and IL-10 serum concentrations were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
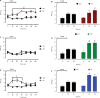
Results: Both CFX and CA induced a significant thermal antiallodynic effect 3 and 24 h after administration. Furthermore, CA induced a mechanical antiallodynic effect 30, 60, and 90 min after administration. Moreover, a significant anti-inflammatory effect was found for both molecules 24 h after Carr injection. Also, both CA and CFX modulated TNF-α and IL-10 serum concentrations at different times.
Conclusion: Our results provide evidence that both CFX and CA cause an analgesic effect on a Carr inflammatory pain model and that said analgesic effect differs between each β-lactam molecule. Furthermore, this effect may be related to an anti-inflammatory effect of both molecules and a direct TNF-α and IL-10 serum concentration modulation.
Keywords: TNF-α concentration; analgesic effect; antiallodynic properties; ceftriaxone; clavulanic acid; inflammatory pain; β-lactam molecules.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Saudagar PS, Survase SA, Singhal RS. Clavulanic acid: a review. Biotechnol Adv. 2008;26(4):335–351. - PubMed
-
- Hu Y, Li W, Lu L, et al. An anti-nociceptive role for ceftriaxone in chronic neuropathic pain in rats. Pain. 2010;148(2):284–301. - PubMed
-
- Macaluso A, Bernabucci M, Trabucco A, et al. Analgesic effect of a single preoperative dose of the antibiotic ceftriaxone in humans. J Pain. 2013;14(6):604–612. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

