Recent advances in the understanding and management of cystic fibrosis pulmonary exacerbations
- PMID: 29862015
- PMCID: PMC5954331
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.13926.1
Recent advances in the understanding and management of cystic fibrosis pulmonary exacerbations
Abstract
Pulmonary exacerbations are common events in cystic fibrosis and have a profound impact on quality of life, morbidity, and mortality. Pulmonary exacerbation outcomes remain poor and a significant proportion of patients fail to recover their baseline lung function despite receiving aggressive treatment with intravenous antibiotics. This focused review provides an update on some of the recent advances that have taken place in our understanding of the epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of pulmonary exacerbations in cystic fibrosis as well as direction for future study.
Keywords: cystic fibrosis; exacerbations; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
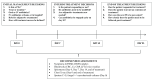
Similar articles
-
Pulmonary Exacerbations in Children with Cystic Fibrosis.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015 Nov;12 Suppl 2:S200-6. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201502-098AW. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2015. PMID: 26595740 Review.
-
Characterization of Inpatient Cystic Fibrosis Pulmonary Exacerbations.Pediatrics. 2017 Feb;139(2):e20162642. doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-2642. Pediatrics. 2017. PMID: 28126911 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Factors associated with response to treatment of pulmonary exacerbations in cystic fibrosis patients.J Cyst Fibros. 2015 Nov;14(6):755-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jcf.2015.01.007. Epub 2015 Feb 14. J Cyst Fibros. 2015. PMID: 25690407 Clinical Trial.
-
Pulmonary artery enlargement and cystic fibrosis pulmonary exacerbations: a cohort study.Lancet Respir Med. 2016 Aug;4(8):636-645. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(16)30105-9. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Lancet Respir Med. 2016. PMID: 27298019 Free PMC article.
-
Management of pulmonary exacerbations in cystic fibrosis: still an unmet medical need in clinical practice.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2015 Apr;9(2):183-94. doi: 10.1586/17476348.2015.1016504. Epub 2015 Feb 18. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2015. PMID: 25692532 Review.
Cited by
-
Standards of Nutritional Care for Patients with Cystic Fibrosis: A Methodological Primer and AGREE II Analysis of Guidelines.Children (Basel). 2021 Dec 14;8(12):1180. doi: 10.3390/children8121180. Children (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943375 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of the Local Inflammatory Environment on Mucosal Vitamin D Metabolism and Signaling in Chronic Inflammatory Lung Diseases.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 10;11:1433. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01433. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32754156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
State-of-the-Art Review: Transformative Changes in the Care of People With Cystic Fibrosis: Implications for Infectious Diseases Specialists.Clin Infect Dis. 2025 Jun 4;80(5):e65-e77. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaf009. Clin Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40465484 Review.
-
Pulmonary Exacerbations in Adults With Cystic Fibrosis: A Grown-up Issue in a Changing Cystic Fibrosis Landscape.Chest. 2021 Jan;159(1):93-102. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.09.084. Epub 2020 Sep 20. Chest. 2021. PMID: 32966813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progressive Scoliosis in a Child with Cystic Fibrosis.Case Rep Pediatr. 2019 Apr 10;2019:1471879. doi: 10.1155/2019/1471879. eCollection 2019. Case Rep Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31093403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Patient Registry: 2015 Annual Report.Bethesda, Maryland.2016. Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. Reference Source
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

