Effect of integrin α5β1 inhibition on SDF-l/CXCR4-mediated choroidal neovascularization
- PMID: 29862169
- PMCID: PMC5957022
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2018.05.04
Effect of integrin α5β1 inhibition on SDF-l/CXCR4-mediated choroidal neovascularization
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the roles of integrins in choroidal neovascularization (CNV) and their associations with the stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 axis.
Methods: CNV lesions were induced in mice using laser photocoagulation. After CNV induction, all animals were randomly assigned to: control, SDF-1, SDF-1+age-related macular degeneration (AMD) 3100 (CXCR4 inhibitor), and SDF-1+ATN161 (integrin α5β1 inhibitor) groups; their effects on CNV progression were observed using hematoxylin eosin (HE) staining, fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA) grading and optical coherence tomography (OCT), and their effects on CXCR4/integrin α5 expression were evaluated using Western blot and double immunofluorescence staining. Hypoxia-exposed endothelial cells (ECs) were used to simulate CNV in vitro, they were treated with SDF-1, combined with CXCR4 siRNA/AMD3100 or ATN161, and expression of integrin α5, cell migration and tube formation were analyzed.
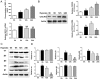
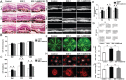
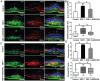
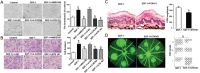
Results: Integrin subunit α5 increased at 3rd and 7th day and decreased at 14th day in CNV mice, with no significant change of β1-integrin. CXCR4 expression in CNV mice had persistent increase within 14d after induction. SDF-1 treatment significantly promoted the CNV progression during 3-14d. The mean CNV length in AMD3100 and ATN161 group at day 7 was 270.13 and 264.23 µm in HE images, significantly lower than the mean length in SDF-1 (345.70 µm) group. AMD3100 and ATN161 also significantly reduced thickness and leakage of CNV induced by SDF-1. Mean integrin α5 positive area in SDF-1 group reached 2.31×104 µm2, significantly higher than control (1.25×104 µm2), which decreased to 1.78×104 µm2 after AMD3100 treatment. About 61.36% of ECs in CNV lesions expressed α5 in SDF-1 group, which significantly decreased to 43.12% after AMD3100 treatment. In vitro, integrin α5 peaked by 6 folds after 6h of hypoxia exposure and CXCR4 gradually increased by up to 2.3 folds after 24h of hypoxia. Approximately 25.12% of ECs expressed integrin α5 after SDF-1 stimulation, which decreased to 7.2%-9.5% after si-CXCR4 or AMD3100 treatment. ATN161 exerted an inhibitory effect comparable to that of si-CXCR4 on EC migration and tube formation in the presence of SDF-1.
Conclusion: SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling induces integrin α5β1 expression in ECs to promote CNV.
Keywords: CXCR4; choroidal neovascularization; endothelial cells; hypoxia; integrin α5β1; stromal cell-derived factor-1.
Figures



References
-
- Zhang ZX, Wang YS, Shi YY, Hou HY, Zhang C, Cai Y, Dou GR, Yao LB, Li FY. Hypoxia specific SDF-1 expression by retinal pigment epithelium initiates bone marrow-derived cells to participate in choroidal neovascularization in a laser-induced mouse model. Curr Eye Res. 2011;36(9):838–849. - PubMed
-
- Feng L, Ju M, Lee KYV, Mackey A, Evangelista M, Iwata D, Adamson P, Lashkari K, Foxton R, Shima D, Ng YS. A proinflammatory function of toll-like receptor 2 in the retinal pigment epithelium as a novel target for reducing choroidal neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration. Am J Pathol. 2017;187(10):2208–2221. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
