The search for gene-gene interactions in genome-wide association studies: challenges in abundance of methods, practical considerations, and biological interpretation
- PMID: 29862246
- PMCID: PMC5952010
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2018.04.05
The search for gene-gene interactions in genome-wide association studies: challenges in abundance of methods, practical considerations, and biological interpretation
Abstract
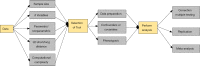
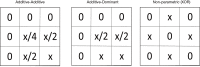
One of the primary goals in this era of precision medicine is to understand the biology of human diseases and their treatment, such that each individual patient receives the best possible treatment for their disease based on their genetic and environmental exposures. One way to work towards achieving this goal is to identify the environmental exposures and genetic variants that are relevant to each disease in question, as well as the complex interplay between genes and environment. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have allowed for a greater understanding of the genetic component of many complex traits. However, these genetic effects are largely small and thus, our ability to use these GWAS finding for precision medicine is limited. As more and more GWAS have been performed, rather than focusing only on common single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and additive genetic models, many researchers have begun to explore alternative heritable components of complex traits including rare variants, structural variants, epigenetics, and genetic interactions. While genetic interactions are a plausible reality that could explain some of the heritabliy that has not yet been identified, especially when one considers the identification of genetic interactions in model organisms as well as our understanding of biological complexity, still there are significant challenges and considerations in identifying these genetic interactions. Broadly, these can be summarized in three categories: abundance of methods, practical considerations, and biological interpretation. In this review, we will discuss these important elements in the search for genetic interactions along with some potential solutions. While genetic interactions are theoretically understood to be important for complex human disease, the body of evidence is still building to support this component of the underlying genetic architecture of complex human traits. Our hope is that more sophisticated modeling approaches and more robust computational techniques will enable the community to identify these important genetic interactions and improve our ability to implement precision medicine in the future.
Keywords: Epistasis; data mining; genetic interactions; statistical methods.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A practical view of fine-mapping and gene prioritization in the post-genome-wide association era.Open Biol. 2020 Jan;10(1):190221. doi: 10.1098/rsob.190221. Epub 2020 Jan 15. Open Biol. 2020. PMID: 31937202 Free PMC article.
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Characterizing genetic interactions in human disease association studies using statistical epistasis networks.BMC Bioinformatics. 2011 Sep 12;12:364. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-364. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21910885 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Interactions in Human Disease Studies-Evidence Is Mounting.Annu Rev Biomed Data Sci. 2023 Aug 10;6:377-395. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biodatasci-102022-120818. Epub 2023 May 17. Annu Rev Biomed Data Sci. 2023. PMID: 37196359 Review.
-
Exploiting the proteome to improve the genome-wide genetic analysis of epistasis in common human diseases.Hum Genet. 2008 Aug;124(1):19-29. doi: 10.1007/s00439-008-0522-8. Epub 2008 Jun 13. Hum Genet. 2008. PMID: 18551320 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of tree-based statistical learning methods for constructing genetic risk scores.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Mar 21;23(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-04634-w. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 35313824 Free PMC article.
-
Facilitating Complex Trait Analysis via Reduced Complexity Crosses.Trends Genet. 2020 Aug;36(8):549-562. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2020.05.003. Epub 2020 May 29. Trends Genet. 2020. PMID: 32482413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Large-Scale Genome-Wide Association Study of Epistasis Effects of Production Traits and Daughter Pregnancy Rate in U.S. Holstein Cattle.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jul 18;12(7):1089. doi: 10.3390/genes12071089. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356105 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the Pathogenicity, Penetrance, and Expressivity of Putative Disease-Causing Variants in a Population Setting.Am J Hum Genet. 2019 Feb 7;104(2):275-286. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.12.015. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Am J Hum Genet. 2019. PMID: 30665703 Free PMC article.
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms in angiogenesis-related genes and outcomes from antiangiogenic therapies in renal cell carcinoma: really a step towards personalized oncology, or not at all?Ann Transl Med. 2019 Mar;7(Suppl 1):S15. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.01.51. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31032296 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
