Metformin Inhibits Mouse Islet Insulin Secretion and Alters Intracellular Calcium in a Concentration-Dependent and Duration-Dependent Manner near the Circulating Range
- PMID: 29862303
- PMCID: PMC5971297
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/9163052
Metformin Inhibits Mouse Islet Insulin Secretion and Alters Intracellular Calcium in a Concentration-Dependent and Duration-Dependent Manner near the Circulating Range
Abstract
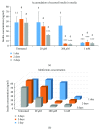
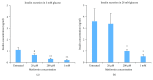
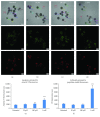
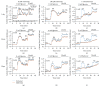
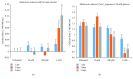
Metformin is considered the first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes. While metformin primarily increases insulin sensitivity, evidence also suggests that metformin affects the activity of insulin-secreting pancreatic islets. This study was designed to systematically examine the direct effects of metformin by measuring insulin secretion and the kinetics of the calcium response to glucose stimulation in isolated mouse islets using varying concentrations (20 μM, 200 μM, and 1 mM) and durations (~1, 2, and 3 days) of metformin exposure. We observed both concentration- and duration-dependent inhibitory effects of metformin. Concentrations as little as 20 μM (nearing circulating therapeutic levels) were sufficient to reduce insulin secretion following 3-day treatment. Concentrations of 200 μM and 1 mM produced more pronounced effects more rapidly. With 1 mM metformin, islets showed severe impairments in calcium handling, inhibition of insulin secretion, and increased cell death. No stimulatory effects of metformin were observed for any experimental endpoint. We conclude that the direct effects of metformin on islets are inhibitory at near-physiological concentrations. Beneficial effects of metformin observed on islets under various stressors may occur by "resting" fatigued cellular processes. However, metformin may have unintended consequences on normally functioning islets within the circulating range that require further evaluation.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

