History and current status of polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column for treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock
- PMID: 29863114
- PMCID: PMC5881300
- DOI: 10.1002/ags3.12015
History and current status of polymyxin B-immobilized fiber column for treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock
Abstract
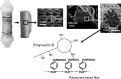
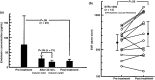
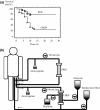
Toraymyxin® (Toray Medical Co., Ltd, Tokyo, Japan) has been developed as a direct hemoperfusion column that contains polymyxin B-immobilized fiber to bind endotoxins in patients' blood. Toraymyxin was approved by the Japanese National Health Insurance system for the treatment of endotoxemia and septic shock in 1994. Since then, PMX (defined as direct hemoperfusion with Toraymyxin) has been safely used in more than 100 000 cases in emergency and intensive care units in Japan. Toraymyxin is currently available for use in clinical settings in 12 countries outside of Japan. We reviewed and analyzed the development, clinical use, and efficacy of Toraymyxin, and assessed the current status of Toraymyxin use for the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. Our review shows that PMX appeared to be effective in improving hemodynamics and respiratory function in septic shock requiring emergency abdominal surgery. Recent large-scale ranomized controlled trialscould not demonstrate whether prognosis is improved by PMX. However, the latest meta-analysis revealed that PMX significantly decreased mortality in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. Combination of PMX with continuous hemodiafiltration and longer duration of PMX might be an effective strategy to improve survival in such patients.
Keywords: Toraymyxin; blood purification; direct hemoperfusion with Toraymyxin (PMX); endotoxin; sepsis.
Figures



References
-
- Anspach FB. Endotoxin removal by affinity sorbents. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 2001;49:665–81. - PubMed
-
- Aoki H, Kodama M, Tani T, Hanasawa K. Treatment of sepsis by extracorporeal elimination of endotoxin using polymyxin b‐immobilized fiber. Am J Surg. 1994;167:412–7. - PubMed
-
- Shoji H. Extracorporeal endotoxin removal for the treatment of sepsis: endotoxin adsorption cartridge (toraymyxin). Ther Apher Dial. 2003;7:108–14. - PubMed
-
- Vincent JL, Laterre PF, Cohen J, et al. A pilot‐controlled study of a polymyxin b‐immobilized hemoperfusion cartridge in patients with severe sepsis secondary to intra‐abdominal infection. Shock. 2005;23:400–5. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

