Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis of d-amphetamine in an attention task in rodents
- PMID: 29864032
- PMCID: PMC6076339
- DOI: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000409
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis of d-amphetamine in an attention task in rodents
Abstract
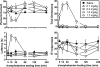
Amphetamine is a common therapeutic agent for alleviating the core symptoms associated with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adults. The current study used a translational model of attention, the five-choice serial reaction time (5-CSRT) procedure with rats, to examine the time-course effects of d-amphetamine. Effects of different dosages of d-amphetamine were related to drug-plasma concentrations, fashioned after comprehensive pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic assessments that have been employed in clinical investigations. We sought to determine whether acute drug-plasma concentrations that enhance performance in the 5-CSRT procedure are similar to those found to be therapeutic in patients diagnosed with ADHD. Results from the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic assessment indicate that d-amphetamine plasma concentrations associated with improved performance on the 5-CSRT procedure overlap with those that have been reported to be therapeutic in clinical trials. The current findings suggest that the 5-CSRT procedure may be a useful preclinical model for predicting the utility of novel ADHD therapeutics and their effective concentrations.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
No conflicts are declared.
Figures
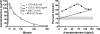
References
-
- Bachmann CJ, Wijlaars L, Kalverdijk LJ, Burcu M, Glaeske G, Schiling-Veninga CCM, Hoffmann F, Aagaard L, Zito JM. Trends in ADHD medication use in children and adolescents in five western countries, 2005–2012. Euro Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017;27:484–93. - PubMed
-
- Berridge CW, Devilbiss DM, Andrzejewski ME, Arnsten AFT, Kelley AE, Schmeichel B, Hamilton C, Spencer RC. Methylphenidate preferentially increases catecholamine neurotransmission within the prefrontal cortex at low doses that enhance cognitive function. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;60:1111–20. - PubMed
-
- Biederman J, Petty CR, Woodworth KY, Lomedico A, Hyder LL, Faraone SV. Adult outcome of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a controlled 16-year follow-up study. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012;73:941–50. - PubMed
-
- Bizzaro L, Stolerman IP. Attentional effects of nicotine and amphetamine in rats at different levels of motivation. Psychopharmacol. 2003;170:271–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

