Irinotecan and Δ⁸-Tetrahydrocannabinol Interactions in Rat Liver: A Preliminary Evaluation Using Biochemical and Genotoxicity Markers
- PMID: 29865166
- PMCID: PMC6100385
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23061332
Irinotecan and Δ⁸-Tetrahydrocannabinol Interactions in Rat Liver: A Preliminary Evaluation Using Biochemical and Genotoxicity Markers
Abstract
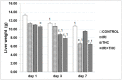
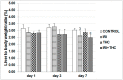
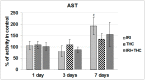
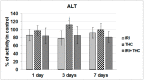
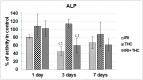
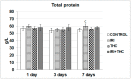
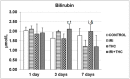
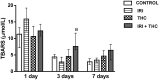
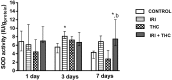
There is growing interest regarding the use of herbal preparations based on Cannabis sativa for medicinal purposes, despite the poorly understood interactions of their main constituent Δ⁸-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) with conventional drugs, especially cytostatics. The objective of this pilot study was to prove whether the concomitant intake of THC impaired liver function in male Wistar rats treated with the anticancer drug irinotecan (IRI), and evaluate the toxic effects associated with this exposure. IRI was administered once intraperitoneally (at 100 mg/kg of the body weight (b.w.)), while THC was administered per os repeatedly for 1, 3, and 7 days (at 7 mg/kg b.w.). Functional liver impairments were studied using biochemical markers of liver function (aspartate aminotransferase-AST, alanine aminotransferase-ALP, alkaline phosphatase-AP, and bilirubin) in rats given a combined treatment, single IRI, single THC, and control groups. Using common oxidative stress biomarkers, along with measurement of primary DNA damage in hepatocytes, the degree of impairments caused at the cellular level was also evaluated. THC caused a time-dependent enhancement of acute toxicity in IRI-treated rats, which was confirmed by body and liver weight reduction. Although single THC affected ALP and AP levels more than single IRI, the levels of liver function markers measured after the administration of a combined treatment mostly did not significantly differ from control. Combined exposure led to increased oxidative stress responses in 3- and 7-day treatments, compared to single IRI. Single IRI caused the highest DNA damage at all timepoints. Continuous 7-day oral exposure to single THC caused an increased mean value of comet tail length compared to its shorter treatments. Concomitant intake of THC slightly affected the levels of IRI genotoxicity at all timepoints, but not in a consistent manner. Further studies are needed to prove our preliminary observations, clarify the underlying mechanisms behind IRI and THC interactions, and unambiguously confirm or reject the assumptions made herein.
Keywords: cannabinoid-based preparations; functional liver impairments; genotoxicity; hepatocytes; liver to body weight ratio; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- ElSohly M.A. Chemical Constituents of Cannabis. In: Grotenhermen F., Russo E., editors. Cannabis and Cannabinoids: Pharmacology,Toxicology, and Therapeutic Potential. Volume 1. The Haworth Press Inc.; Binghamton, NY, USA: 2002. pp. 27–35.
-
- Mathijssen R.H.J., Van Alphen R.J., Verweij J., Loos W.J., Nooter K., Stoter G., Sparreboom A. Clinical pharmacokinetics and metabolism of irinotecan (CPT-11) Clin. Cancer Res. 2001;7:2182–2194. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

