Receptor⁻Receptor Interactions in Multiple 5-HT1A Heteroreceptor Complexes in Raphe-Hippocampal 5-HT Transmission and Their Relevance for Depression and Its Treatment
- PMID: 29865267
- PMCID: PMC6099659
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23061341
Receptor⁻Receptor Interactions in Multiple 5-HT1A Heteroreceptor Complexes in Raphe-Hippocampal 5-HT Transmission and Their Relevance for Depression and Its Treatment
Abstract
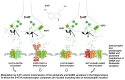
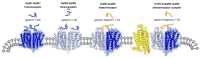
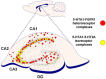
Due to the binding to a number of proteins to the receptor protomers in receptor heteromers in the brain, the term "heteroreceptor complexes" was introduced. A number of serotonin 5-HT1A heteroreceptor complexes were recently found to be linked to the ascending 5-HT pathways known to have a significant role in depression. The 5-HT1A⁻FGFR1 heteroreceptor complexes were involved in synergistically enhancing neuroplasticity in the hippocampus and in the dorsal raphe 5-HT nerve cells. The 5-HT1A protomer significantly increased FGFR1 protomer signaling in wild-type rats. Disturbances in the 5-HT1A⁻FGFR1 heteroreceptor complexes in the raphe-hippocampal 5-HT system were found in a genetic rat model of depression (Flinders sensitive line (FSL) rats). Deficits in FSL rats were observed in the ability of combined FGFR1 and 5-HT1A agonist cotreatment to produce antidepressant-like effects. It may in part reflect a failure of FGFR1 treatment to uncouple the 5-HT1A postjunctional receptors and autoreceptors from the hippocampal and dorsal raphe GIRK channels, respectively. This may result in maintained inhibition of hippocampal pyramidal nerve cell and dorsal raphe 5-HT nerve cell firing. Also, 5-HT1A⁻5-HT2A isoreceptor complexes were recently demonstrated to exist in the hippocampus and limbic cortex. They may play a role in depression through an ability of 5-HT2A protomer signaling to inhibit the 5-HT1A protomer recognition and signaling. Finally, galanin (1⁻15) was reported to enhance the antidepressant effects of fluoxetine through the putative formation of GalR1⁻GalR2⁻5-HT1A heteroreceptor complexes. Taken together, these novel 5-HT1A receptor complexes offer new targets for treatment of depression.
Keywords: G protein-coupled receptors; depression; fibroblast growth factor receptor; galanin; heteroreceptor complexes; oligomerization; receptor tyrosine kinase; receptor-receptor interactions; serotonin 5-HT1A receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Agnati L.F., Fuxe K., Benfenati F., Celani M.F., Battistini N., Mutt V., Cavicchioli L., Galli G., Hokfelt T. Differential modulation by CCK-8 and CCK-4 of [3H]spiperone binding sites linked to dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors in the brain of the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 1983;35:179–183. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90547-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fuxe K., Agnati L.F., Benfenati F., Celani M., Zini I., Zoli M., Mutt V. Evidence for the existence of receptor—Receptor interactions in the central nervous system. Studies on the regulation of monoamine receptors by neuropeptides. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 1983;18:165–179. - PubMed
-
- Fuxe K., Marcellino D., Borroto-Escuela D.O., Frankowska M., Ferraro L., Guidolin D., Ciruela F., Agnati L.F. The changing world of G protein-coupled receptors: From monomers to dimers and receptor mosaics with allosteric receptor-receptor interactions. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 2010;30:272–283. doi: 10.3109/10799893.2010.506191. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

