Quantitative imaging of brain energy metabolisms and neuroenergetics using in vivo X-nuclear 2H, 17O and 31P MRS at ultra-high field
- PMID: 29866434
- PMCID: PMC5996770
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmr.2018.05.005
Quantitative imaging of brain energy metabolisms and neuroenergetics using in vivo X-nuclear 2H, 17O and 31P MRS at ultra-high field
Abstract
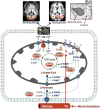
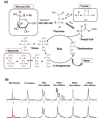
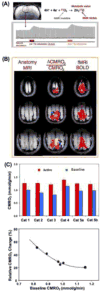
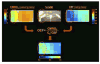
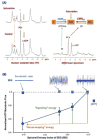
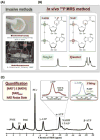
Brain energy metabolism relies predominantly on glucose and oxygen utilization to generate biochemical energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is essential for maintaining basal electrophysiological activities in a resting brain and supporting evoked neuronal activity under an activated state. Studying complex neuroenergetic processes in the brain requires sophisticated neuroimaging techniques enabling noninvasive and quantitative assessment of cerebral energy metabolisms and quantification of metabolic rates. Recent state-of-the-art in vivo X-nuclear MRS techniques, including 2H, 17O and 31P MRS have shown promise, especially at ultra-high fields, in the quest for understanding neuroenergetics and brain function using preclinical models and in human subjects under healthy and diseased conditions.
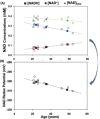
Keywords: Brain energy metabolism; Cerebral metabolic rate of glucose (CMR(Glc)) and oxygen (CMRO(2)) consumption, and ATP production (CMR(ATP)); In vivo X-nuclear MRS and imaging; NAD redox state; Neuroenergetics; TCA cycle rate (V(TCA)); Ultra-high magnetic field (UHF).
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Siesjo BK. Brain energy metabolism. Wiley; New York: 1978.
-
- Shulman RG, Rothman DL, Behar KL, Hyder F. Energetic basis of brain activity: implications for neuroimaging. Trends Neurosci. 2004;27:489–495. - PubMed
-
- Zhu XH, Du F, Zhang N, Lu M, Zhang Y, Liu X, Lei H, Zhang XL, Ugurbil K, Chen W. Study of Brain Bioenergetics and Function using In Vivo MRS. In: Kamil Ugurbil KU, Berliner Lawrence, editors. Biological magnetic Resonance: fMRI: From Nuclear Spins to Brain Function. Springer; New York: 2015. pp. 819–864.
-
- Hyder F, Patel AB, Gjedde A, Rothman DL, Behar KL, Shulman RG. Neuronal-glial glucose oxidation and glutamatergic-GABAergic function. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006;26:865–877. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

