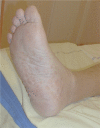
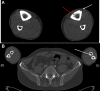
Unexplained bone pain and sexual addiction
- PMID: 29866696
- PMCID: PMC5990071
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-225380
Unexplained bone pain and sexual addiction
Keywords: bone and joint infections; sexual transmitted infections (bacterial).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Kidd S, Torrone E, Su J, et al. . Reported primary and secondary syphilis cases in the United States: implications for HIV Infection. Sex Transm Dis. In Press 2018. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000810 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Park KH, Lee MS, Hong IK, et al. . Bone involvement in secondary syphilis: a case report and systematic review of the literature. Sex Transm Dis 2014;41:532–7. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000164 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
