Comprehensive comparative analysis of 5'-end RNA-sequencing methods
- PMID: 29867192
- PMCID: PMC6075671
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-018-0014-2
Comprehensive comparative analysis of 5'-end RNA-sequencing methods
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Comprehensive comparative analysis of 5'-end RNA-sequencing methods.Nat Methods. 2018 Dec;15(12):1126. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0237-2. Nat Methods. 2018. PMID: 30459407
Abstract
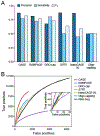
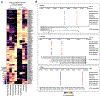
Specialized RNA-seq methods are required to identify the 5' ends of transcripts, which are critical for studies of gene regulation, but these methods have not been systematically benchmarked. We directly compared six such methods, including the performance of five methods on a single human cellular RNA sample and a new spike-in RNA assay that helps circumvent challenges resulting from uncertainties in annotation and RNA processing. We found that the 'cap analysis of gene expression' (CAGE) method performed best for mRNA and that most of its unannotated peaks were supported by evidence from other genomic methods. We applied CAGE to eight brain-related samples and determined sample-specific transcription start site (TSS) usage, as well as a transcriptome-wide shift in TSS usage between fetal and adult brain.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

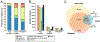
References
-
- Heinzen EL, Neale BM, Traynelis SF, Allen AS & Goldstein DB The genetics of neuropsychiatric diseases: looking in and beyond the exome. Annu Rev Neurosci 38, 47–68 (2015). - PubMed
-
- De Gobbi M et al. A regulatory SNP causes a human genetic disease by creating a new transcriptional promoter. Science 312, 1215–1217 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Davuluri RV, Suzuki Y, Sugano S, Plass C & Huang TH The functional consequences of alternative promoter use in mammalian genomes. Trends Genet 24, 167–177 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Grob TJ et al. Human delta Np73 regulates a dominant negative feedback loop for TAp73 and p53. Cell Death Differ 8, 1213–1223 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

