Psychological Predictors of Visual and Auditory P300 Brain-Computer Interface Performance
- PMID: 29867319
- PMCID: PMC5960704
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00307
Psychological Predictors of Visual and Auditory P300 Brain-Computer Interface Performance
Abstract
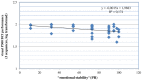
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) provide communication channels independent from muscular control. In the current study we used two versions of the P300-BCI: one based on visual the other on auditory stimulation. Up to now, data on the impact of psychological variables on P300-BCI control are scarce. Hence, our goal was to identify new predictors with a comprehensive psychological test-battery. A total of N = 40 healthy BCI novices took part in a visual and an auditory BCI session. Psychological variables were measured with an electronic test-battery including clinical, personality, and performance tests. The personality factor "emotional stability" was negatively correlated (Spearman's rho = -0.416; p < 0.01) and an output variable of the non-verbal learning test (NVLT), which can be interpreted as ability to learn, correlated positively (Spearman's rho = 0.412; p < 0.01) with visual P300-BCI performance. In a linear regression analysis both independent variables explained 24% of the variance. "Emotional stability" was also negatively related to auditory P300-BCI performance (Spearman's rho = -0.377; p < 0.05), but failed significance in the regression analysis. Psychological parameters seem to play a moderate role in visual P300-BCI performance. "Emotional stability" was identified as a new predictor, indicating that BCI users who characterize themselves as calm and rational showed worse BCI performance. The positive relation of the ability to learn and BCI performance corroborates the notion that also for P300 based BCIs learning may constitute an important factor. Further studies are needed to consolidate or reject the presented predictors.
Keywords: NVLT; auditory P300-BCI; emotional stability; predictors; visual P300-BCI.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Psychological predictors of SMR-BCI performance.Biol Psychol. 2012 Jan;89(1):80-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2011.09.006. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Biol Psychol. 2012. PMID: 21964375
-
Prediction of auditory and visual p300 brain-computer interface aptitude.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e53513. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053513. Epub 2013 Feb 14. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23457444 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Emotional Stimulations on the Online Operation of a P300-Based Brain-Computer Interface.Front Hum Neurosci. 2021 Feb 26;15:612777. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.612777. eCollection 2021. Front Hum Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33767615 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control.Clin Neurophysiol. 2002 Jun;113(6):767-91. doi: 10.1016/s1388-2457(02)00057-3. Clin Neurophysiol. 2002. PMID: 12048038 Review.
-
Human visual skills for brain-computer interface use: a tutorial.Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2020 Oct;15(7):799-809. doi: 10.1080/17483107.2020.1754929. Epub 2020 Jun 1. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2020. PMID: 32476516 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
P300 Speller Performance Predictor Based on RSVP Multi-feature.Front Hum Neurosci. 2019 Jul 30;13:261. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2019.00261. eCollection 2019. Front Hum Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31417382 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Prefrontal Single-Channel EEG Data for Portable Auditory ERP-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces.Front Hum Neurosci. 2019 Jul 25;13:250. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2019.00250. eCollection 2019. Front Hum Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31404255 Free PMC article.
-
A Regional Smoothing Block Sparse Bayesian Learning Method With Temporal Correlation for Channel Selection in P300 Speller.Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 Jun 10;16:875851. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.875851. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35754766 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing and computing humans by means of the brain using Brain-Computer Interfaces - understanding the user - previous evidence, self-relevance and the user's self-concept as potential superordinate human factors of relevance.Front Hum Neurosci. 2024 Feb 16;17:1286895. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1286895. eCollection 2023. Front Hum Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38435127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural mechanisms of training an auditory event-related potential task in a brain-computer interface context.Hum Brain Mapp. 2019 Jun 1;40(8):2399-2412. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24531. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Hum Brain Mapp. 2019. PMID: 30693612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allison B. Z., Faller J., Neuper C. (2012). BCIs that use steady-state visual evoked potentials or slow cortical potentials, in Brain-Computer Interfaces: Principles and Practice, eds. Wolpaw J. R., Wolpaw E. W. (New York, NY: Oxford University Press; ), 241–249.
-
- Averbeck M., Leiberich P., Grote-Kusch M. T., Olbrich E., Schröder A., Brieger M., et al. (1997). Skalen zur Erfassung der Lebensqualität (SEL) - Manual. Frankfurt: Swets & Zeitlinger B.V.; Swets Test Services.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

