Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs on Spontaneous Recurrent Seizures in a Novel Model of Extended Hippocampal Kindling in Mice
- PMID: 29867462
- PMCID: PMC5968120
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00451
Effects of Antiepileptic Drugs on Spontaneous Recurrent Seizures in a Novel Model of Extended Hippocampal Kindling in Mice
Abstract
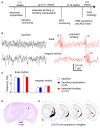
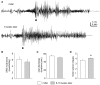
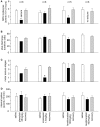
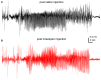
Epilepsy is a common neurological disorder characterized by naturally-occurring spontaneous recurrent seizures and comorbidities. Kindling has long been used to model epileptogenic mechanisms and to assess antiepileptic drugs. In particular, extended kindling can induce spontaneous recurrent seizures without gross brain lesions, as seen clinically. To date, the development of spontaneous recurrent seizures following extended kindling, and the effect of the antiepileptic drugs on these seizures are not well understood. In the present study we aim to develop a mouse model of extended hippocampal kindling for the first time. Once established, we plan to evaluate the effect of three different antiepileptic drugs on the development of the extended-hippocampal-kindled-induced spontaneous recurrent seizures. Male C57 black mice were used for chronic hippocampal stimulations or handling manipulations (twice daily for up to 70 days). Subsequently, animals underwent continuous video/EEG monitoring for seizure detection. Spontaneous recurrent seizures were consistently observed in extended kindled mice but no seizures were detected in the control animals. The aforementioned seizures were generalized events characterized by hippocampal ictal discharges and concurrent motor seizures. Incidence and severity of the seizures was relatively stable while monitored over a few months after termination of the hippocampal stimulation. Three antiepileptic drugs with distinct action mechanisms were tested: phenytoin, lorazepam and levetiracetam. They were applied via intra-peritoneal injections at anticonvulsive doses and their effects on the spontaneous recurrent seizures were analyzed 10-12 h post-injection. Phenytoin (25 mg/kg) and levetiracetam (400 mg/kg) abolished the spontaneous recurrent seizures. Lorazepam (1.5 mg/kg) decreased motor seizure severity but did not reduce the incidence and duration of corresponding hippocampal discharges, implicating its inhibitory effects on seizure spread. No gross brain lesions were observed in a set of extended hippocampal kindled mice submitted to histological evaluation. All these data suggests that our model could be considered as a novel mouse model of extended hippocampal kindling. Some limitations remain to be considered.
Keywords: antiepileptic drugs; convulsion; electroencephalograph (EEG); epilepsy; hippocampus; kindling; mice; spontaneous seizures.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impaired Spatial Learning and Memory in Middle-Aged Mice with Kindling-Induced Spontaneous Recurrent Seizures.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Sep 24;10:1077. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01077. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31611787 Free PMC article.
-
Clustering of Spontaneous Recurrent Seizures in a Mouse Model of Extended Hippocampal Kindling.Front Neurol. 2021 Nov 25;12:738986. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.738986. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34899563 Free PMC article.
-
Convulsive behaviors of spontaneous recurrent seizures in a mouse model of extended hippocampal kindling.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Dec 23;16:1076718. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.1076718. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36620863 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the piriform cortex in kindling.Prog Neurobiol. 1996 Dec;50(5-6):427-81. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0082(96)00036-6. Prog Neurobiol. 1996. PMID: 9015822 Review.
-
Chemical Kindling as an Experimental Model to Assess the Conventional Drugs in the Treatment of Post-traumatic Epilepsy.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2023;22(10):1417-1428. doi: 10.2174/1871527322666221128155813. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2023. PMID: 36443981 Review.
Cited by
-
Delta-fast ripple coupling suppression: designing a brain-mimetic stimulation paradigm for seizure abolishment.Front Neurosci. 2025 Jun 24;19:1619278. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1619278. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40630858 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling of post-traumatic epilepsy and experimental research aimed at its prevention.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2020 Dec 18;54(2):e10656. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X202010656. eCollection 2020. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2020. PMID: 33331416 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic Reshaping and Neuronal Outcomes in the Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 8;22(8):3860. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083860. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33917911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduced Effect of Anticonvulsants on AMPA Receptor Palmitoylation-Deficient Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 18;12:711737. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.711737. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34483921 Free PMC article.
-
Observations From a Mouse Model of Forebrain Voa1 Knockout: Focus on Hippocampal Structure and Function.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Nov 21;13:484. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00484. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31824264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bertram E. H. (2017). Monitoring for seizures in rodents, in Models of Seizures and Epilepsy, 2nd edn, eds Pitkänen A., Buckmaster P. S., Galanopoulou A. S., Moshé L. S. (London, UK: Academic Press; ), 97–110.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

