Prenatal Lipopolysaccharide Exposure Promotes Dyslipidemia in the Male Offspring Rats
- PMID: 29867579
- PMCID: PMC5964359
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00542
Prenatal Lipopolysaccharide Exposure Promotes Dyslipidemia in the Male Offspring Rats
Abstract
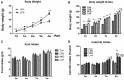
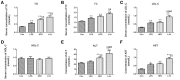
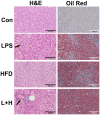
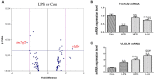
Inflammation is critical to the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). We have uncovered intrauterine inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) increases CVDs in adult offspring rats. The present study aimed to explore the role of prenatal exposure to LPS on the lipid profiles in male offspring rats and to further assess their susceptibility to high fat diet (HFD). Maternal LPS (0.79 mg/kg) exposure produced a significant increase in serum and hepatic levels of total cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, aspartate amino transferase as well as liver morphological abnormalities in 8-week-old offspring rats. Meanwhile, disturbed gene expressions involved in hepatic lipid metabolism and related signaling pathways were found, especially the up-regulated very-low density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR) and down-regulated transmembrane 7 superfamily member 2 (TM7SF2). Following HFD treatment, however, the lipid profile shifts and liver dysfunction were exacerbated compared to the offsprings treated with prenatal LPS exposure alone. Compared with that in control offsprings, the hepatic mitochondria (Mt) in offspring rats solely treated with HFD exhibited remarkably higher ATP level, enforced Complex IV expression and a sharp reduction of its activity, whereas the offsprings from LPS-treated dams showed the loss of ATP content, diminished membrane potential, decline in protein expression and activity of mitochondrial respiratory complex IV, increased level of MtDNA deletion as well. Furthermore, treatment with HFD deteriorated these mitochondrial disorders in the prenatally LPS-exposed offspring rats. Taken together, maternal LPS exposure reinforces dyslipidemia in response to a HFD in adult offsprings, which should be associated with mitochondrial abnormalities and disturbed gene expressions of cholesterol metabolism.
Keywords: dyslipidemia; inflammation; intrauterine environment; mitochondrion; offspring.
Figures



References
-
- American Heart Association Nutrition Committee. Lichtenstein A. H., Appel L. J., Brands M., Carnethon M., Daniels S., et al. (2006). Diet and lifestyle recommendations revision 2006: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Nutrition Committee. Circulation 14, 82–96. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.176158 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

