Exosomes in cancer: small vesicular transporters for cancer progression and metastasis, biomarkers in cancer therapeutics
- PMID: 29868251
- PMCID: PMC5983002
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.4763
Exosomes in cancer: small vesicular transporters for cancer progression and metastasis, biomarkers in cancer therapeutics
Abstract
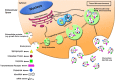
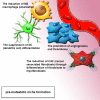
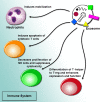
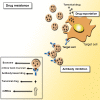
Cancer progression is a polygenic procedure in which the exosomes can function as substantial roles. Exosomes are tiny, phospholipid bilayer membrane nanovesicles of endocytic derivation with a diameter of 40-100 nm. These nanovesicles can transport bioactive molecules containing mRNAs, proteins, DNA fragments, and non-coding RNAs from a donor cell to recipient cells, and cause the alteration in genetic and epigenetic factors and reprogramming of the target cells. Many diverse cell types such as mesenchymal cells, immune cells, and cancer cells can induce the release of exosomes. Increasing evidence illustrated that the exosomes derived from tumor cells might trigger the tumor initiation, tumor cell growth and progression, metastasis, and drug resistance. The secreted nanovesicles of exosomes can play significant roles in cells communicate via shuttling the nucleic acid molecules and proteins to target cells and tissues. In this review, we discussed multiple mechanisms related to biogenesis, load, and shuttle of the exosomes. Also, we illustrated the diverse roles of exosomes in several types of human cancer development, tumor immunology, angiogenesis, and metastasis. The exosomes may act as the promising biomarkers for the prognosis of various types of cancers which suggested a new pathway for anti-tumor therapeutic of these nanovesicles and promoted exosome-based cancer for clinical diagnostic and remedial procedures.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Cancer; Exosome; Metastasis; Therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

