Anti-quorum Sensing Activities of Selected Coral Symbiotic Bacterial Extracts From the South China Sea
- PMID: 29868500
- PMCID: PMC5951975
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00144
Anti-quorum Sensing Activities of Selected Coral Symbiotic Bacterial Extracts From the South China Sea
Abstract
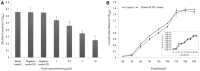
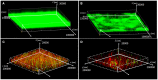
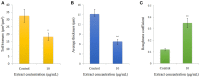
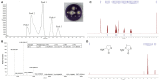
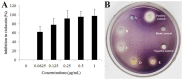
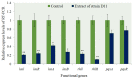
The worldwide increase in antibiotic-resistant pathogens means that identification of alternative antibacterial drug targets and the subsequent development of new treatment strategies are urgently required. One such new target is the quorum sensing (QS) system. Coral microbial consortia harbor an enormous diversity of microbes, and are thus rich sources for isolating novel bioactive and pharmacologically valuable natural products. However, to date, the versatility of their bioactive compounds has not been broadly explored. In this study, about two hundred bacterial colonies were isolated from a coral species (Pocillopora damicornis) and screened for their ability to inhibit QS using the bioreporter strain Chromobacterium violaceum ATCC 12472. Approximately 15% (30 isolates) exhibited anti-QS activity, against the indicator strain. Among them, a typical Gram-positive bacterium, D11 (Staphylococcus hominis) was identified and its anti-QS activity was investigated. Confocal microscopy observations showed that the bacterial extract inhibited the biofilm formation of clinical isolates of wild-type P. aeruginosa PAO1 in a dose-dependent pattern. Chromatographic separation led to the isolation of a potent QS inhibitor that was identified by high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy as DL-homocysteine thiolactone. Gene expression analyses using RT-PCR showed that strain D11 led to a significant down-regulation of QS regulatory genes (lasI, lasR, rhlI, and rhlR), as well as a virulence-related gene (lasB). From the chemical structure, the target compound (DL-homocysteine thiolactone) is an analog of the acyl-homoserine lactones (AHLs), and we presume that DL-homocysteine thiolactone outcompetes AHL in occupying the receptor and thereby inhibiting QS. Whole-genome sequence analysis of S. hominis D11 revealed the presence of predicted genes involved in the biosynthesis of homocysteine thiolactone. This study indicates that coral microbes are a resource bank for developing QS inhibitors and they will facilitate the discovery of new biotechnologically relevant compounds that could be used instead of traditional antibiotics.
Keywords: HPLC-MS-NMR; S. hominis; anti-quorum sensing; coral microbes; marine drug.
Figures
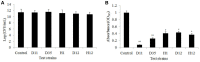
Similar articles
-
Antibiofilm activity substances derived from coral symbiotic bacterial extract inhibit biofouling by the model strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1.Microb Biotechnol. 2018 Nov;11(6):1090-1105. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13312. Epub 2018 Oct 9. Microb Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30298548 Free PMC article.
-
Mosloflavone attenuates the quorum sensing controlled virulence phenotypes and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1: In vitro, in vivo and in silico approach.Microb Pathog. 2019 Jun;131:128-134. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.04.005. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30959097
-
Anti-quorum Sensing and Anti-biofilm Activity of Delftia tsuruhatensis Extract by Attenuating the Quorum Sensing-Controlled Virulence Factor Production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jul 26;7:337. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00337. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28798903 Free PMC article.
-
An evolving perspective on the Pseudomonas aeruginosa orphan quorum sensing regulator QscR.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Oct 28;4:152. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00152. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25389523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quorum Sensing: A Prospective Therapeutic Target for Bacterial Diseases.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Apr 4;2019:2015978. doi: 10.1155/2019/2015978. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31080810 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quorum Sensing Inhibitory and Quenching Activity of Bacillus cereus RC1 Extracts on Soft Rot-Causing Bacteria Lelliottia amnigena.ACS Omega. 2022 Jul 11;7(29):25291-25308. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c02202. eCollection 2022 Jul 26. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35910130 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of antibiofilm and quorum quenching potencies of environmental bacteria in controlling biofilm of food spoilage bacteria.BMC Res Notes. 2025 Feb 17;18(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13104-025-07141-2. BMC Res Notes. 2025. PMID: 39962543 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Oceans for Curative Compounds: Potential New Antimicrobial and Anti-Virulence Molecules against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Mar Drugs. 2022 Dec 23;21(1):9. doi: 10.3390/md21010009. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 36662182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa inhibits quorum-sensing mechanisms of soft rot pathogen Lelliottia amnigena RCE to regulate its virulence factors and biofilm formation.Front Microbiol. 2022 Aug 23;13:977669. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.977669. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36090086 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum Sensing Inhibitors: Curbing Pathogenic Infections through Inhibition of Bacterial Communication.Iran J Pharm Res. 2021 Spring;20(2):486-514. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2020.113470.14318. Iran J Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 34567177 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

