Effectiveness of Long-Acting Injectable vs Oral Antipsychotics in Patients With Schizophrenia: A Meta-analysis of Prospective and Retrospective Cohort Studies
- PMID: 29868849
- PMCID: PMC5890463
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbx090
Effectiveness of Long-Acting Injectable vs Oral Antipsychotics in Patients With Schizophrenia: A Meta-analysis of Prospective and Retrospective Cohort Studies
Abstract
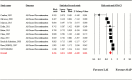
Compared with oral antipsychotics (OAPs), long-acting injectable antipsychotics (LAIs) should improve medication adherence and reduce relapses in schizophrenia. However, meta-analyses of randomized trials and mirror-image studies yielded inconsistent results. Nonrandomized cohort studies with parallel comparisons of LAIs and OAPs offer a third design to examine this issue. We meta-analyzed cohort studies with ≥24 weeks duration and hospitalization data. Primary outcome was hospitalization rate, ie, number of hospitalizations per person-year. Secondary outcomes included hospitalization risk, ie, proportion of patients experiencing ≥1 hospitalizations, all-cause discontinuation, and total hospitalization days. Patient severity and/or chronicity at baseline was also meta-analyzed and explored as a potential effect size moderator. Altogether, 42 studies (n = 101 624; follow-up = 18.6 ± 10.0 mo) were meta-analyzed. LAIs were superior to OAPs regarding hospitalization rate (studies = 15, person-years = 68 009, rate ratio = 0.85, 95% CI = 0.78-0.93, P < .001) and all-cause discontinuations (studies = 10, n = 37 293, risk ratio = 0.78, 95% CI = 0.67-0.91, P = .001), but not regarding hospitalization risk (studies = 33, n = 51 733, risk ratio = 0.92, 95% CI = 0.84-1.00, P = .06), and hospitalization days (studies = 11, n = 21 328, Hedges' g = -0.05, 95% CI = -0.16 to 0.06, P = .39). Illness severity/chronicity was significantly greater in patients prescribed LAIs vs OAPs when all available information was pooled together (studies = 23, n = 61 806, Hedges' g = 0.15, 95% CI = 0.03-0.26, P = .01), but not when examined separately. In summary, this meta-analysis of cohort studies, which included patients that are broadly representative of clinical practice, indicates that LAIs are superior to OAPs. The lack of significant superiority of LAIs for hospitalization risk and hospital days needs to be interpreted in the context of naturalistic treatment selection with subsequently greater illness severity/chronicity in LAI-treated patients.
Figures



References
-
- Lieberman JA, Perkins D, Belger A et al. . The early stages of schizophrenia: speculations on pathogenesis, pathophysiology, and therapeutic approaches. Biol Psychiatry. 2001;50:884–897. - PubMed
-
- van Haren NE, Hulshoff Pol HE, Schnack HG et al. . Focal gray matter changes in schizophrenia across the course of the illness: a 5-year follow-up study. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2007;32:2057–2066. - PubMed
-
- Robinson D, Woerner MG, Alvir JM et al. . Predictors of relapse following response from a first episode of schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1999;56:241–247. - PubMed
-
- Leucht S, Barnes TR, Kissling W, Engel RR, Correll C, Kane JM. Relapse prevention in schizophrenia with new-generation antipsychotics: a systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Am J Psychiatry. 2003;160:1209–1222. - PubMed
-
- Leucht S, Arbter D, Engel RR, Kissling W, Davis JM. How effective are second-generation antipsychotic drugs? A meta-analysis of placebo-controlled trials. Mol Psychiatry. 2009;14:429–447. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

