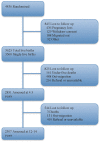
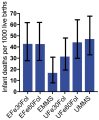
Cohort Profile: The Maternal and Infant Nutrition Interventions in Matlab (MINIMat) cohort in Bangladesh
- PMID: 29868907
- PMCID: PMC6280939
- DOI: 10.1093/ije/dyy102
Cohort Profile: The Maternal and Infant Nutrition Interventions in Matlab (MINIMat) cohort in Bangladesh
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maternal Micronutrient Supplementation and Long Term Health Impact in Children in Rural Bangladesh.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 18;11(8):e0161294. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161294. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27537051 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of prenatal food and micronutrient interventions on under-five mortality and stunting: Analysis of data from the MINIMat randomized trial, Bangladesh.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 15;13(2):e0191260. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191260. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29447176 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of invitation to food supplementation early in pregnancy combined with multiple micronutrients on infant survival: analysis of data from MINIMat randomized trial, Bangladesh.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2015 May 28;15:125. doi: 10.1186/s12884-015-0551-y. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2015. PMID: 26018633 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nutrition and maternal, neonatal, and child health.Semin Perinatol. 2015 Aug;39(5):361-72. doi: 10.1053/j.semperi.2015.06.009. Epub 2015 Jul 10. Semin Perinatol. 2015. PMID: 26166560 Review.
-
Micronutrient deficiencies and effect of supplements on correcting them.Nestle Nutr Workshop Ser Pediatr Program. 2011;68:127-34; discussion 134-40. doi: 10.1159/000325777. Epub 2011 Oct 3. Nestle Nutr Workshop Ser Pediatr Program. 2011. PMID: 22044896 Review.
Cited by
-
A scientometric analysis of birth cohorts in South Asia: Way forward for Pakistan.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 9;15(7):e0235385. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235385. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32645067 Free PMC article.
-
Association between maternal haemoglobin status during pregnancy and children's mental and psychomotor development at 18 months of age: Evidence from rural Bangladesh.Glob Health Action. 2024 Dec 31;17(1):2390269. doi: 10.1080/16549716.2024.2390269. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Glob Health Action. 2024. PMID: 39193768 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Experience of Domestic Violence, Associations with Children's Lipid Biomarkers at 10 Years: Findings from MINIMat Study in Rural Bangladesh.Nutrients. 2019 Apr 23;11(4):910. doi: 10.3390/nu11040910. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31018615 Free PMC article.
-
PSICA: Decision trees for probabilistic subgroup identification with categorical treatments.Stat Med. 2019 Sep 30;38(22):4436-4452. doi: 10.1002/sim.8308. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Stat Med. 2019. PMID: 31246349 Free PMC article.
-
Perspective: Growth Monitoring and Promotion as an Opportunity to Improve Early Childhood Development.Adv Nutr. 2025 Aug;16(8):100470. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2025.100470. Epub 2025 Jun 25. Adv Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40578560 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Underwood BA. Health and nutrition in women, infants, and children: overview of the global situation and the Asian enigma. Nutr Rev 2002;60(5 Pt 2):S7–13. - PubMed
-
- Shrimpton R, Victora CG, de Onis M, Lima RC, Blössner M, Clugston G.. Worldwide timing of growth faltering: implications for nutritional interventions. Pediatrics 2001;107:E75.. - PubMed
-
- Victora CG, de Onis M, Hallal PC, Blössner M, Shrimpton R.. Worldwide timing of growth faltering: revisiting implications for interventions. Pediatrics 2010;125:e473–80. - PubMed
-
- Leroy JL, Ruel M, Habicht J-P, Frongillo EA.. Linear growth deficit continues to accumulate beyond the first 1000 days in low- and middle-income countries: global evidence from 51 national surveys. J Nutr 2014;144:1460–66. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

