Dracunculiasis Eradication: Are We There Yet?
- PMID: 29869608
- PMCID: PMC6090361
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.18-0204
Dracunculiasis Eradication: Are We There Yet?
Abstract
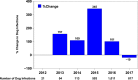
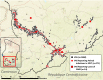
This report summarizes the status of the global Dracunculiasis Eradication Program as of the end of 2017. Dracunculiasis (guinea worm disease) has been eliminated from 19 of 21 countries where it was endemic in 1986, when an estimated 3.5 million cases occurred worldwide. Only Chad and Ethiopia reported cases in humans, 15 each, in 2017. Infections of animals, mostly domestic dogs, with Dracunculus medinensis were reported in those two countries and also in Mali. Insecurity and infections in animals are the two main obstacles remaining to interrupting dracunculiasis transmission completely.
Figures


References
-
- Watts SJ, 1987. Dracunculiasis in Africa: its geographic extent, incidence and at-risk population. Am J Trop Med Hyg 37: 119–125. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization , 2004. Dracunculiasis eradication: Geneva declaration on Guinea-worm eradication, Geneva, 2004. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 79: 234–235. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

