Bioinformatics core competencies for undergraduate life sciences education
- PMID: 29870542
- PMCID: PMC5988330
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0196878
Bioinformatics core competencies for undergraduate life sciences education
Abstract
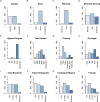
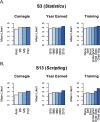
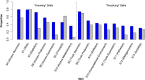
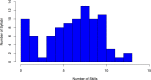
Although bioinformatics is becoming increasingly central to research in the life sciences, bioinformatics skills and knowledge are not well integrated into undergraduate biology education. This curricular gap prevents biology students from harnessing the full potential of their education, limiting their career opportunities and slowing research innovation. To advance the integration of bioinformatics into life sciences education, a framework of core bioinformatics competencies is needed. To that end, we here report the results of a survey of biology faculty in the United States about teaching bioinformatics to undergraduate life scientists. Responses were received from 1,260 faculty representing institutions in all fifty states with a combined capacity to educate hundreds of thousands of students every year. Results indicate strong, widespread agreement that bioinformatics knowledge and skills are critical for undergraduate life scientists as well as considerable agreement about which skills are necessary. Perceptions of the importance of some skills varied with the respondent's degree of training, time since degree earned, and/or the Carnegie Classification of the respondent's institution. To assess which skills are currently being taught, we analyzed syllabi of courses with bioinformatics content submitted by survey respondents. Finally, we used the survey results, the analysis of the syllabi, and our collective research and teaching expertise to develop a set of bioinformatics core competencies for undergraduate biology students. These core competencies are intended to serve as a guide for institutions as they work to integrate bioinformatics into their life sciences curricula.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that author TMS has an affiliation with a private company, Digital World Biology (DWB). As noted in the updated Funding Statement, DWB provided support for this work in the form of salary for TMS. This affiliation does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures


References
-
- National Research Council. BIO2010: transforming undergraduate education for future research biologists Washington: National Academies Press; 2003. Available from: https://doi.org/10.17226/10497 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bialek W, Botstein D. Introductory science and mathematics education for 21st-century biologists. Science. 2004;303:788–90. doi: 10.1126/science.1095480 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lopatto D, Alvarez C, Barnard D, Chandrasekaran C, Chung H-M, Du C, et al. Undergraduate research: Genomics Education Partnership. Science. 2008;322:684–85. doi: 10.1126/science.1165351 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Campbell AM, Ledbetter MLS, Hoopes LLM, Eckdahl TT, Heyer LJ, Rosenwald A, et al. Genome Consortium for Active Teaching: meeting the goals of BIO2010. CBE Life Sci Educ. 2007;6:109–18. doi: 10.1187/cbe.06-10-0196 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

