A novel diindolylmethane analog, 1,1-bis(3'-indolyl)-1-(p-chlorophenyl) methane, inhibits the tumor necrosis factor-induced inflammatory response in primary murine synovial fibroblasts through a Nurr1-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 29870816
- PMCID: PMC6138555
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.05.024
A novel diindolylmethane analog, 1,1-bis(3'-indolyl)-1-(p-chlorophenyl) methane, inhibits the tumor necrosis factor-induced inflammatory response in primary murine synovial fibroblasts through a Nurr1-dependent mechanism
Abstract
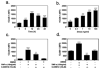
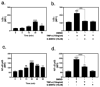
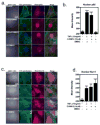
The progression of rheumatoid arthritis involves the thickening of the synovial lining due to the proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) and infiltration by inflammatory cells. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine involved in progression of the disease. Under rheumatoid conditions, FLS express the tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-recognition complex (TNFR1, TNFR2, VCAM-1 and ICAM-1), which induces local macrophage activation and leads to downstream nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling. The NF-κB-regulated inflammatory gene, cyclooxygenase (COX), increases synthesis of prostaglandins that contribute to the propagation of inflammatory damage within the joint. Because the nuclear orphan receptor, NR4A2 (Nurr1), can negatively regulate NF-κB-dependent inflammatory gene expression in macrophages, we postulated that activation of this receptor by the Nurr1 ligand 1,1-bis(3'-indolyl)-1-(p-chlorophenyl) methane (C-DIM12) would modulate inflammatory gene expression in synovial fibroblasts by inhibiting NF-κB. Treatment with C-DIM12 suppressed TNFα-induced expression of adhesion molecules and NF-κB regulated genes in primary synovial fibroblasts including vascular adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1), PGE2 and COX-2. Immunofluorescence studies indicated that C-DIM12 did not prevent translocation of p65 and stabilized nuclear localization of Nurr1 in synovial fibroblasts. Knockdown of Nurr1 expression by RNA interference prevented the inhibitory effects of C-DIM12 on inflammatory gene expression, indicating that the anti-inflammatory effects of this compound are Nurr1-dependent. Collectively, these data suggest that this receptor may be a viable therapeutic target in RA.
Keywords: C-DIM12; NF-κB; Nurr1; Rheumatoid arthritis; Synovial fibroblast; TNFα.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Nurr1 Activator 1,1-Bis(3'-Indolyl)-1-(p-Chlorophenyl)Methane Blocks Inflammatory Gene Expression in BV-2 Microglial Cells by Inhibiting Nuclear Factor κB.Mol Pharmacol. 2015 Jun;87(6):1021-34. doi: 10.1124/mol.114.095398. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Mol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25858541 Free PMC article.
-
The Nurr1 Ligand,1,1-bis(3'-Indolyl)-1-(p-Chlorophenyl)Methane, Modulates Glial Reactivity and Is Neuroprotective in MPTP-Induced Parkinsonism.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018 Jun;365(3):636-651. doi: 10.1124/jpet.117.246389. Epub 2018 Apr 6. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018. PMID: 29626009 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of nuclear orphan receptor NURR1 transcription by NF-kappa B and cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate response element-binding protein in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue.J Immunol. 2002 Mar 15;168(6):2979-87. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.6.2979. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11884470
-
Structure-dependent activation of gene expression by bis-indole and quinoline-derived activators of nuclear receptor 4A2.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2019 Oct;94(4):1711-1720. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13564. Epub 2019 Jul 21. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2019. PMID: 31102570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potent synthetic and endogenous ligands for the adopted orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1.Exp Mol Med. 2021 Jan;53(1):19-29. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00555-5. Epub 2021 Jan 21. Exp Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33479411 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Geniposide on Regulating the Functions of Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts via Inhibiting Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptors1/3 Coupling Gαi/Gαs Conversion.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Dec 8;11:584176. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.584176. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33363467 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an imidazole salt catalytic system for the preparation of bis(indolyl)methanes and bis(naphthyl)methane.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 25;14(4):e0216008. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216008. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31022274 Free PMC article.
-
Orphan Nuclear Receptor NR4A2 Is Constitutively Expressed in Cartilage and Upregulated in Inflamed Synovium From hTNF-Alpha Transgenic Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Apr 20;13:835697. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.835697. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35529439 Free PMC article.
-
3,3'-Diindolylmethane and indole-3-carbinol: potential therapeutic molecules for cancer chemoprevention and treatment via regulating cellular signaling pathways.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Aug 26;23(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03031-4. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37633886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative safety, pharmacokinetics, and off-target assessment of 1,1-bis(3'-indolyl)-1-(p-chlorophenyl) methane in mouse and dog: implications for therapeutic development.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024 Apr 21;13(2):tfae059. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfae059. eCollection 2024 Apr. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024. PMID: 38655145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aherne CM, McMorrow J, Kane D, FitzGerald O, Mix KS, Murphy EP. Identification of NR4A2 as a transcriptional activator of IL-8 expression in human inflammatory arthritis. Molecular Immunology. 2009;46(16):3345–3357. - PubMed
-
- Armaka M, Gkretsi V, Kontoyiannis D, Kollias G. A standardized protocol for the isolation and culture of normal and arthritogenic murine synovial fibroblasts 2009
-
- Bonta PI, van Tiel CM, Vos M, Pols TWH, van Thienen JV, Ferreira V, et al. Nuclear receptors Nur77, Nurr1, and NOR-1 expressed in atherosclerotic lesion macrophages reduce lipid loading and inflammatory responses. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2006;26(10):2288–2294. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

