Tempol Protects Against Acute Renal Injury by Regulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR and GSK3β Signaling Cascades and Afferent Arteriolar Activity
- PMID: 29870982
- PMCID: PMC6065105
- DOI: 10.1159/000490338
Tempol Protects Against Acute Renal Injury by Regulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR and GSK3β Signaling Cascades and Afferent Arteriolar Activity
Abstract
Background/aims: Free radical scavenger tempol is a protective antioxidant against ischemic injury. Tubular epithelial apoptosis is one of the main changes in the renal ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. Meanwhile some proteins related with apoptosis and inflammation are also involved in renal I/R injury. We tested the hypothesis that tempol protects against renal I/R injury by activating protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin (PKB, Akt/mTOR) and glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β) pathways as well as the coordinating apoptosis and inflammation related proteins.
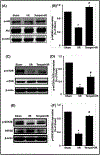
Methods: The right renal pedicle of C57Bl/6 mouse was clamped for 30 minutes and the left kidney was removed in the study. The renal injury was assessed with serum parameters by an automatic chemistry analyzer. Renal expressions of Akt/mTOR and GSK3β pathways were measured by western blot in I/R mice treated with saline or tempol (50mg/kg) and compared with sham-operated mice.
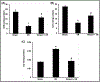
Results: The levels of blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine and superoxide anion (O2.-) increased, and superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) decreased significantly after renal I/R injury. However, tempol treatment prevented the changes. Besides, I/R injury reduced renal expression of p-Akt, p-GSK3β, p-mTOR, Bcl2 and increased NF-κB, p-JNK and p53 in kidney, tempol significantly normalized these changes. In addition, renal I/R injury reduced the response of afferent arteriole to Angiotensin II (Ang II), while tempol treatment improved the activity of afferent arteriole.
Conclusion: Tempol attenuates renal I/R injury. The protective mechanisms seem to relate with activation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR and GSK3β pathways, inhibition of cellular damage markers and inflammation factors, as well as improvement of afferent arteriolar activity.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Afferent arteriole; Ischemia/reperfusion; Tempol.
© 2018 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure Statement
The authors of this manuscript state that they do not have any conflict of interests and nothing to disclose.
Figures

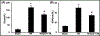



Similar articles
-
Protective Effect of Tempol on Acute Kidney Injury Through PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway.Kidney Blood Press Res. 2016;41(2):129-138. doi: 10.1159/000443414. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2016. PMID: 26894882 Free PMC article.
-
Tempol attenuates renal fibrosis in mice with unilateral ureteral obstruction: the role of PI3K-Akt-FoxO3a signaling.J Korean Med Sci. 2014 Feb;29(2):230-7. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.2.230. Epub 2014 Jan 28. J Korean Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 24550650 Free PMC article.
-
Propofol can suppress renal ischemia-reperfusion injury through the activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signal pathway.Gene. 2019 Aug 5;708:14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.05.023. Epub 2019 May 10. Gene. 2019. PMID: 31082504
-
Apoptosis repressor with caspase recruitment domain deficiency accelerates ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-induced acute kidney injury by suppressing inflammation and apoptosis: The role of AKT/mTOR signaling.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Apr;112:108681. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108681. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30970510
-
Pharmacological modulation of PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR/ERK signaling pathways in ischemic injury: a mechanistic perspective.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 Feb 26;40(3):131. doi: 10.1007/s11011-025-01543-8. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 40009091 Review.
Cited by
-
Renoprotective Effect of Pitavastatin against TAA-Induced Renal Injury: Involvement of the miR-93/PTEN/AKT/mTOR Pathway.Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024 Jan 23;2024:6681873. doi: 10.1155/2024/6681873. eCollection 2024. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 38293706 Free PMC article.
-
The miR-15a-5p-XIST-CUL3 regulatory axis is important for sepsis-induced acute kidney injury.Ren Fail. 2019 Nov;41(1):955-966. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2019.1669460. Ren Fail. 2019. PMID: 31658856 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of ELF4 aggravates renal injury in ischemia/reperfusion mice through promotion of pyroptosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, and endoplasmic reticulum stress.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Jul 20;24(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12860-023-00485-2. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37474923 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of miR-21-3p on lung injury in rats with traumatic hemorrhagic shock resuscitated with sodium bicarbonate Ringer's solution.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Dec;10(24):1331. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-5148. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36660723 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA‑93 inhibits the apoptosis and inflammatory response of tubular epithelial cells via the PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway in acute kidney injury.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Sep;24(3):666. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12305. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34296286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Uchino S, Bellomo R, Goldsmith D, Bates S, Ronco C: An assessment of the RIFLE criteria for acute renal failure in hospitalized patients. Crit Care Med 2006;34:1913–1917. - PubMed
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, Bouman C, Macedo E, Gibney N, Tolwani A, Ronco C, Beginning, Ending Supportive Therapy for the Kidney I: Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA 2005;294:813–818. - PubMed
-
- Liangos O, Wald R, O’Bell JW, Price L, Pereira BJ, Jaber BL: Epidemiology and outcomes of acute renal failure in hospitalized patients: a national survey. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2006;1:43–51. - PubMed
-
- Ali T, Khan I, Simpson W, Prescott G, Townend J, Smith W, Macleod A: Incidence and outcomes in acute kidney injury: a comprehensive population-based study. J Am Soc Nephrol 2007;18:1292–1298. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

