Variable number of TMC1-dependent mechanotransducer channels underlie tonotopic conductance gradients in the cochlea
- PMID: 29872055
- PMCID: PMC5988745
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04589-8
Variable number of TMC1-dependent mechanotransducer channels underlie tonotopic conductance gradients in the cochlea
Abstract
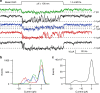
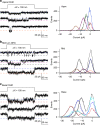
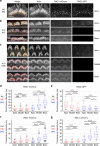
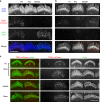
Functional mechanoelectrical transduction (MET) channels of cochlear hair cells require the presence of transmembrane channel-like protein isoforms TMC1 or TMC2. We show that TMCs are required for normal stereociliary bundle development and distinctively influence channel properties. TMC1-dependent channels have larger single-channel conductance and in outer hair cells (OHCs) support a tonotopic apex-to-base conductance gradient. Each MET channel complex exhibits multiple conductance states in ~50 pS increments, basal MET channels having more large-conductance levels. Using mice expressing fluorescently tagged TMCs, we show a three-fold increase in number of TMC1 molecules per stereocilium tip from cochlear apex to base, mirroring the channel conductance gradient in OHCs. Single-molecule photobleaching indicates the number of TMC1 molecules per MET complex changes from ~8 at the apex to ~20 at base. The results suggest there are varying numbers of channels per MET complex, each requiring multiple TMC1 molecules, and together operating in a coordinated or cooperative manner.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Lim DJ, Anniko M. Developmental morphology of the mouse inner ear. A scanning electron microscopic observation. Acta Otolaryngol. Suppl. 1985;422:1–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

