Proton-pump inhibitors among adults: a nationwide drug-utilization study
- PMID: 29872455
- PMCID: PMC5977421
- DOI: 10.1177/1756284818777943
Proton-pump inhibitors among adults: a nationwide drug-utilization study
Abstract
Background: The use of proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) has grown worldwide, and there are concerns about increased unsubstantiated long-term use. The aim of the study was to describe the real-world use of PPIs over the past decade in an entire national population.
Methods: This was a nationwide population-based drug-utilization study. Patterns of outpatient PPI use among adults in Iceland between 2003 and 2015 were investigated, including annual incidence and prevalence, duration of use, and dose of tablet used (lower versus higher), as well as the proportion of PPI use attributable to gastroprotection.
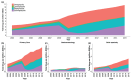
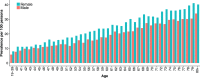
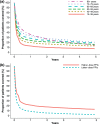
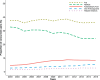
Results: We observed 1,372,790 prescription fills over the entire study period, of which 95% were for higher-dose PPIs. Annual incidence remained stable across time (3.3-4.1 per 100 persons per year), while the annual prevalence increased from 8.5 per 100 persons to 15.5 per 100 persons. Prevalence increased with patient age and was higher among women than men. Duration of treatment increased with patients' age (36% of users over 80 years remained on treatment after 1 year compared with 13% of users aged 19-39 years), and was longer among those initiating on a higher dose compared with a lower dose. The proportion of PPI users concurrently using nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs decreased over the study period, while the proportion concurrently using acetylsalicylic acid, oral anticoagulants, or platelet inhibitors increased.
Conclusions: In this nationwide study, a considerable increase in overall outpatient use of PPIs over a 13-year period was observed, particularly among older adults. Patients were increasingly treated for longer durations than recommended by clinical guidelines and mainly with higher doses.
Keywords: incidence; nationwide; pharmacoepidemiology; prevalence; proton-pump inhibitors; treatment duration.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest in preparing this article.
Figures

Comment in
-
Proton pump inhibitor-induced subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus.Dermatol Ther. 2022 Dec;35(12):e15959. doi: 10.1111/dth.15959. Epub 2022 Nov 6. Dermatol Ther. 2022. PMID: 36284259 No abstract available.
References
-
- Raghunath AS, Hungin AP, Mason J, et al. Symptoms in patients on long-term proton pump inhibitors: prevalence and predictors. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2009; 29: 431–439. - PubMed
-
- Lundell L, Miettinen P, Myrvold HE, et al. Comparison of outcomes twelve years after antireflux surgery or omeprazole maintenance therapy for reflux esophagitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009; 7: 1292–1298. - PubMed
-
- Mahon D, Rhodes M, Decadt B, et al. Randomized clinical trial of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication compared with proton-pump inhibitors for treatment of chronic gastro-oesophageal reflux. Br J Surg 2005; 92: 695–699. - PubMed
-
- Mehta S, Bennett J, Mahon D, et al. Prospective trial of laparoscopic nissen fundoplication versus proton pump inhibitor therapy for gastroesophageal reflux disease: seven-year follow-up. J Gastrointest Surg 2006; 10: 1312–1316. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

