Evaluation of 230 patients with relapsed/refractory deletion 17p chronic lymphocytic leukaemia treated with ibrutinib from 3 clinical trials
- PMID: 29873072
- PMCID: PMC6120509
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.15421
Evaluation of 230 patients with relapsed/refractory deletion 17p chronic lymphocytic leukaemia treated with ibrutinib from 3 clinical trials
Abstract
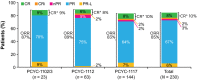
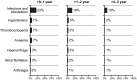
Patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) with deletion 17p [del(17p)] have poor outcomes with chemoimmunotherapy. Ibrutinib is indicated for the treatment of CLL/SLL, including del(17p) CLL/SLL, and allows for treatment without chemotherapy. This integrated analysis was performed to evaluate outcomes in 230 patients with relapsed/refractory del(17p) CLL/SLL from three ibrutinib studies. With a median of 2 prior therapies (range, 1-12), 18% and 79% of evaluable patients had del(11q) or unmutated IGHV, respectively. With a median follow-up of 28 months, overall response rate was 85% and estimated 30-month progression-free and overall survival rates were 57% [95% confidence interval (CI) 50-64] and 69% (95% CI 61-75), respectively. Patients with normal lactate dehydrogenase or no bulky disease had the most favourable survival outcomes. Sustained haematological improvements in haemoglobin, platelet count and absolute neutrophil count occurred in 61%, 67% and 70% of patients with baseline cytopenias, respectively. New onset severe cytopenias and infections decreased in frequency over time. Progression-free and overall survival with ibrutinib surpass those of other therapies for patients with del(17p) CLL/SLL. These results provide further evidence of the robust clinical activity of ibrutinib in difficult-to-treat CLL/SLL populations.
Keywords: 17p deletion; BTK inhibitor; chronic lymphocytic leukaemia; ibrutinib.
© 2018 The Authors. British Journal of Haematology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Badoux, X.C. , Keating, M.J. , Wang, X. , O'Brien, S.M. , Ferrajoli, A. , Faderl, S. , Burger, J. , Koller, C. , Lerner, S. , Kantarjian, H. & Wierda, W.G. (2011) Cyclophosphamide, fludarabine, alemtuzumab, and rituximab as salvage therapy for heavily pretreated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood, 118, 2085–2093. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brejcha, M. , Stoklasova, M. , Brychtova, Y. , Panovska, A. , Stepanovska, K. , Vankova, G. , Plevova, K. , Oltova, A. , Horka, K. , Pospisilova, S. , Mayer, J. & Doubek, M. (2014) Clonal evolution in chronic lymphocytic leukemia detected by fluorescence in situ hybridization and conventional cytogenetics after stimulation with CpG oligonucleotides and interleukin‐2: a prospective analysis. Leukemia Research, 38, 170–175. - PubMed
-
- Burger, J.A. , Keating, M.J. , Wierda, W.G. , Hartmann, E. , Hoellenriegel, J. , Rosin, N.Y. , de Weerdt, I. , Jeyakumar, G. , Ferrajoli, A. , Cardenas‐Turanzas, M. , Lerner, S. , Jorgensen, J.L. , Nogueras‐Gonzalez, G.M. , Zacharian, G. , Huang, X. , Kantarjian, H. , Garg, N. , Rosenwald, A. & O'Brien, S. (2014) Safety and activity of ibrutinib plus rituximab for patients with high‐risk chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a single‐arm, phase 2 study. The Lancet Oncology, 15, 1090–1099. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Byrd, J.C. , Furman, R.R. , Coutre, S.E. , Flinn, I.W. , Burger, J.A. , Blum, K.A. , Grant, B. , Sharman, J.P. , Coleman, M. , Wierda, W.G. , Jones, J.A. , Zhao, W. , Heerema, N.A. , Johnson, A.J. , Sukbuntherng, J. , Chang, B.Y. , Clow, F. , Hedrick, E. , Buggy, J.J. , James, D.F. & O'Brien, S. (2013) Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. New England Journal of Medicine, 369, 32–42. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

