Dosing optimization of CCR4 immunotoxin for improved depletion of CCR4+ Treg in nonhuman primates
- PMID: 29873181
- PMCID: PMC6068354
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12331
Dosing optimization of CCR4 immunotoxin for improved depletion of CCR4+ Treg in nonhuman primates
Abstract
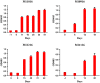
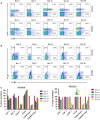
Recently, we have developed a diphtheria toxin-based recombinant anti-human CCR4 immunotoxin for targeting CCR4+ tumors and Tregs. In this study, we further optimized the dosing schedule for improved CCR4+ Treg depletion. We have demonstrated that up to a 90% depletion was achieved and the depletion extended to approximately 2 weeks in the peripheral blood and more than 48 days in the lymph node at 25 μg·kg-1 , BID for 8 consecutive days in cynomolgus monkeys. Expansion was observed including monocytes and NK cells. Antibody against the CCR4 immunotoxin was detected after approximately 2 weeks, affecting further depletion efficacy for multiple course treatment.
Keywords: CCR4; Treg; diphtheria toxin; immunotoxin.
© 2018 The Authors. Published by FEBS Press and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Baluna R and Vitetta ES (1997) Vascular leak syndrome: a side effect of immunotherapy. Immunopharmacology 37, 117–132. - PubMed
-
- Hall BM (2016) CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells in transplantation tolerance: 25 years on. Transplantation 100, 2533–2547. - PubMed
-
- Liu C, Workman CJ and Vignali DA (2016) Targeting regulatory T cells in tumors. FEBS J 283, 2731–2748. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

