Real-time high spatial resolution dose verification in stereotactic motion adaptive arc radiotherapy
- PMID: 29873185
- PMCID: PMC6036363
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12364
Real-time high spatial resolution dose verification in stereotactic motion adaptive arc radiotherapy
Abstract
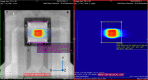
Purpose: Radiation treatments delivered with real-time multileaf collimator (MLC) tracking currently lack fast pretreatment or real-time quality assurance. The purpose of this study is to test a 2D silicon detector, MagicPlate-512 (MP512), in a complex clinical environment involving real-time reconfiguration of the MLC leaves during target tracking.
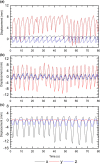
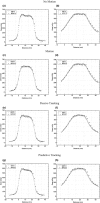
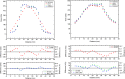
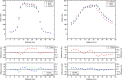
Methods: MP512 was placed in the center of a solid water phantom and mounted on a motion platform used to simulate three different patient motions. Electromagnetic target tracking was implemented using the Calypso system (Varian Medical Systems, Palo Alto, CA, USA) and an MLC tracking software. A two-arc VMAT plan was delivered and 2D dose distributions were reconstructed by MP512, EBT3 film, and the Eclipse treatment planning system (TPS). Dose maps were compared using gamma analysis with 2%/2 mm and 3%/3 mm acceptance criteria. Dose profiles were generated in sup-inf and lateral directions to show the agreement of MP512 to EBT3 and to highlight the efficacy of the MLC tracking system in mitigating the effect of the simulated patient motion.
Results: Using a 3%/3 mm acceptance criterion for 2D gamma analysis, MP512 to EBT3 film agreement was 99% and MP512 to TPS agreement was 100%. For a 2%/2 mm criterion, the agreement was 95% and 98%, respectively. Full width at half maximum and 80%/20% penumbral width of the MP512 and EBT3 dose profiles agreed within 1 mm and 0.5 mm, respectively. Patient motion increased the measured dose profile penumbral width by nearly 2 mm (with respect to the no-motion case); however, the MLC tracking strategy was able to mitigate 80% of this effect.
Conclusions: MP512 is capable of high spatial resolution 2D dose reconstruction during adaptive MLC tracking, including arc deliveries. It shows potential as an effective tool for 2D small field dosimetry and pretreatment quality assurance for MLC tracking modalities. These results provide confidence that detector-based pretreatment dosimetry is clinically feasible despite fast real-time MLC reconfigurations.
Keywords: 2D silicon array; MLC tracking; QA of adaptive radiotherapy; small field dosimetry.
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Figures






Similar articles
-
MagicPlate-512: A 2D silicon detector array for quality assurance of stereotactic motion adaptive radiotherapy.Med Phys. 2015 Jun;42(6):2992-3004. doi: 10.1118/1.4921126. Med Phys. 2015. PMID: 26127052
-
A two dimensional silicon detectors array for quality assurance in stereotactic radiotherapy: MagicPlate-512.Med Phys. 2014 Sep;41(9):091707. doi: 10.1118/1.4892384. Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 25186382
-
Toward real-time verification for MLC tracking treatments using time-resolved EPID imaging.Med Phys. 2021 Mar;48(3):953-964. doi: 10.1002/mp.14675. Epub 2021 Jan 14. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 33354787
-
Influence of the jaw tracking technique on the dose calculation accuracy of small field VMAT plans.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2017 Jan;18(1):186-195. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12029. Epub 2017 Jan 3. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28291941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estimating dose delivery accuracy in stereotactic body radiation therapy: A review of in-vivo measurement methods.Radiother Oncol. 2020 Aug;149:158-167. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2020.05.014. Epub 2020 May 19. Radiother Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32416282 Review.
Cited by
-
Two-dimensional solid-state array detectors: A technique for in vivo dose verification in a variable effective area.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2019 Nov;20(11):88-94. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12744. Epub 2019 Oct 14. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2019. PMID: 31609090 Free PMC article.
-
High spatial resolution dosimetry for radiation oncology with "MagicPlates," a new 976-pixel monolithic silicon detector.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025 Apr;26(4):e70015. doi: 10.1002/acm2.70015. Epub 2025 Mar 13. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40083111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Keall PJ, Mageras GS, Balter JM, et al. The management of respiratory motion in radiation oncology report of AAPM Task Group 76. Med Phys. 2006;33:3874. - PubMed
-
- Giraud P, Garcia R. Respiratory gating for radiotherapy: main technical aspects and clinical benefits. Bull Cancer. 2010; 97:847–856. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

