Identifying a Core Domain Set to Assess Psoriasis in Clinical Trials
- PMID: 29874367
- PMCID: PMC6233740
- DOI: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.1165
Identifying a Core Domain Set to Assess Psoriasis in Clinical Trials
Abstract
Importance: There is no consensus on which domains should be measured or which instruments should be used in clinical trials for psoriasis therapies.
Objective: To achieve international consensus among psoriasis stakeholders on a core set of domains that should be measured in all psoriasis clinical trials.
Design, setting, and participants: Literature review, pre-Delphi survey exercises, nominal group discussions, and audience voting at 4 stakeholder meetings were used to develop candidate domains for 2 rounds of a Delphi survey. Stakeholders were patients or advocates of patients with psoriasis and health care professionals (HCPs) with expertise in psoriasis, including physicians, scientists, advocacy organization representatives, and regulators. Delphi surveys were conducted electronically from October through December 2015 and between September and October 2016. Stakeholder discussions with audience response voting were conducted at live meetings in the United States, Canada, and Italy from January 2013 to December 2016 to refine and ratify the core set of domains.
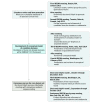
Main outcomes and measures: Two rounds of an electronic Delphi survey were used to determine consensus. A domain was considered "core" (ie, should be measured in all trials) if a threshold consensus of at least 70% was met in both patient and HCP groups. Domains meeting consensus in only 1 group were considered to be important but were not required to be measured in all trials ("middle ring"). These domains were included for rerating in round 2. Domains that did not meet consensus in either of the groups ("outer ring") were considered to be of uncertain importance and were placed in the research agenda.
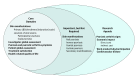
Results: In round 1 of the Delphi survey, 107 HCPs and 14 patients participated. Most HCPs (72 [67%]) were dermatologists between 46 and 64 years old (71 [66%]), white (78 [73%]), and male (75 [70%]) from North America (60 [57%]) and Europe (34 [32%]).There were 10 pharmaceutical industry clinical or health economic scientists, 3 advocacy organization representatives, 2 regulatory agency representatives, and 5 "other." In the second round, 77 HCPs and 15 patients participated. Of the 20 candidate domains, the following 6 met consensus as core domains: skin manifestations, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis symptoms, health-related quality of life, investigator global assessment, patient global assessment, and treatment satisfaction. Secondary skin manifestations as well as nail, inverse, genital, and guttate psoriasis were classified as important but not mandatory. Psoriatic arthritis signs, work productivity or participation, economic impact (direct and indirect cost), and cardiovascular disease comprised the research agenda.
Conclusions and relevance: This iterative Delphi process yielded international consensus among professional and patient stakeholders on 6 domains that should be measured in all clinical trials for psoriasis. Future International Dermatology Outcome Measures group efforts will focus on development of a core outcome measurement set for psoriasis trials.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Core Outcome Sets for Psoriasis Clinical Trials: Definition, Consensus, and Acceptance.JAMA Dermatol. 2018 Oct 1;154(10):1135. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.1166. JAMA Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29874363 No abstract available.
References
-
- Spuls PI, Lecluse LL, Poulsen ML, Bos JD, Stern RS, Nijsten T. How good are clinical severity and outcome measures for psoriasis?: quantitative evaluation in a systematic review. J Invest Dermatol. 2010;130(4):933-943. - PubMed
-
- Gottlieb AB, Armstrong AW. Psoriasis outcome measures: a report from the GRAPPA 2012 annual meeting. J Rheumatol. 2013;40(8):1428-1433. - PubMed
-
- Gottlieb AB, Armstrong AW, Christensen R, et al. The International Dermatology Outcome Measures initiative as applied to psoriatic disease outcomes: a report from the GRAPPA 2013 meeting. J Rheumatol. 2014;41(6):1227-1229. - PubMed
-
- Boers M, Brooks P, Strand CV, Tugwell P. The OMERACT filter for Outcome Measures in Rheumatology. J Rheumatol. 1998;25(2):198-199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

