Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Chronic Venous Disease and Implications for Venoactive Drug Therapy
- PMID: 29874834
- PMCID: PMC6032391
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19061669
Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Chronic Venous Disease and Implications for Venoactive Drug Therapy
Abstract
Chronic venous disease (CVD) is a common pathology, with significant physical and psychological impacts for patients and high economic costs for national healthcare systems. Throughout the last decades, several risk factors for this condition have been identified, but only recently, have the roles of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction been properly assessed. Although still incompletely understood, current knowledge of the pathophysiological mechanisms of CVD reveals several potential targets and strategies for therapeutic intervention, some of which are addressable by currently available venoactive drugs. The roles of these drugs in the clinical improvement of venous tone and contractility, reduction of edema and inflammation, as well as in improved microcirculation and venous ulcer healing have been studied extensively, with favorable results reported in the literature. Here, we aim to review these pathophysiological mechanisms and their implications regarding currently available venoactive drug therapies.
Keywords: MPFF; chronic venous disease; chronic venous insufficiency; endothelial dysfunction; flavonoid; inflammation; micronized purified flavonoid fraction; pathophysiology; venoactive drugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The sponsor reviewed a draft of the manuscript but had no role in the decision to publish the final version.
Figures
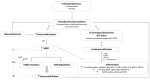
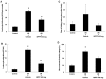
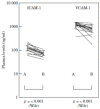
References
-
- Eklof B., Rutherford R.B., Bergan J.J., Carpentier P.H., Gloviczki P., Kistner R.L., Meissner M.H., Moneta G.L., Myers K., Padberg F.T., et al. Revision of the CEAP classification for chronic venous disorders: Consensus statement. J. Vasc. Surg. 2004;40:1248–1252. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2004.09.027. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rabe E., Guex J.J., Puskas A., Scuderi A., Fernandez Quesada F. Epidemiology of chronic venous disorders in geographically diverse populations: Results from the Vein Consult Program. Int. Angiol. 2012;31:105–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

