Oxidized phospholipids are proinflammatory and proatherogenic in hypercholesterolaemic mice
- PMID: 29875409
- PMCID: PMC6033669
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0198-8
Oxidized phospholipids are proinflammatory and proatherogenic in hypercholesterolaemic mice
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Oxidized phospholipids are proinflammatory and proatherogenic in hypercholesterolaemic mice.Nature. 2018 Sep;561(7724):E43. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0313-x. Nature. 2018. PMID: 30013121
Abstract
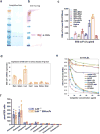
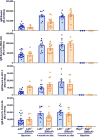
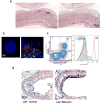
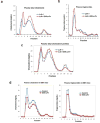
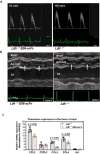
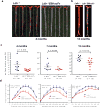
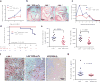
Oxidized phospholipids (OxPL) are ubiquitous, are formed in many inflammatory tissues, including atherosclerotic lesions, and frequently mediate proinflammatory changes 1 . Because OxPL are mostly the products of non-enzymatic lipid peroxidation, mechanisms to specifically neutralize them are unavailable and their roles in vivo are largely unknown. We previously cloned the IgM natural antibody E06, which binds to the phosphocholine headgroup of OxPL, and blocks the uptake of oxidized low-density lipoprotein (OxLDL) by macrophages and inhibits the proinflammatory properties of OxPL2-4. Here, to determine the role of OxPL in vivo in the context of atherogenesis, we generated transgenic mice in the Ldlr-/- background that expressed a single-chain variable fragment of E06 (E06-scFv) using the Apoe promoter. E06-scFv was secreted into the plasma from the liver and macrophages, and achieved sufficient plasma levels to inhibit in vivo macrophage uptake of OxLDL and to prevent OxPL-induced inflammatory signalling. Compared to Ldlr-/- mice, Ldlr -/- E06-scFv mice had 57-28% less atherosclerosis after 4, 7 and even 12 months of 1% high-cholesterol diet. Echocardiographic and histologic evaluation of the aortic valves demonstrated that E06-scFv ameliorated the development of aortic valve gradients and decreased aortic valve calcification. Both cholesterol accumulation and in vivo uptake of OxLDL were decreased in peritoneal macrophages, and both peritoneal and aortic macrophages had a decreased inflammatory phenotype. Serum amyloid A was decreased by 32%, indicating decreased systemic inflammation, and hepatic steatosis and inflammation were also decreased. Finally, the E06-scFv prolonged life as measured over 15 months. Because the E06-scFv lacks the functional effects of an intact antibody other than the ability to bind OxPL and inhibit OxLDL uptake in macrophages, these data support a major proatherogenic role of OxLDL and demonstrate that OxPL are proinflammatory and proatherogenic, which E06 counteracts in vivo. These studies suggest that therapies inactivating OxPL may be beneficial for reducing generalized inflammation, including the progression of atherosclerosis, aortic stenosis and hepatic steatosis.
Figures



Comment in
-
Inflammatory and atherogenic effects of oxidized phospholipids.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2018 Aug;15(8):441. doi: 10.1038/s41569-018-0051-7. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29934578 No abstract available.
References
-
- Friedman P, Horkko S, Steinberg D, Witztum JL, Dennis EA. Correlation of antiphospholipid antibody recognition with the structure of synthetic oxidized phospholipids. Importance of Schiff base formation and aldol condensation. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:7010–7020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL088093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL135737/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL136275/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES010337/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL055798/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086559/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD012303/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL112276/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL020948/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD082567/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007044/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK044838/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL119828/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

