Evaluation of Combined Topical Ozone and Steroid Therapy in Management of Oral Lichen Planus
- PMID: 29875865
- PMCID: PMC5985865
- DOI: 10.3889/oamjms.2018.219
Evaluation of Combined Topical Ozone and Steroid Therapy in Management of Oral Lichen Planus
Abstract
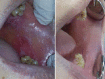
Aim: The present study aims to assess the therapeutic effect of the combination of topical ozone and steroid therapy in comparison to topical ozone alone versus topical steroid as a control in the management of atrophic - erosive oral lichen planus (OLP).
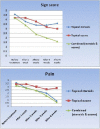
Methods: Sixty-six patients are having atrophic-erosive OLP were included in the study. They were randomly divided into three equal groups to be treated with topical corticosteroids alone (steroid group) as control, topical ozone alone (ozone group) or combination of topical steroids and ozone (combined group). Assessment of pain and sign scores was done before and after each treatment modality.
Results: The results revealed that the greatest significant percentage of change and subsequent improvement in pain and sign scores were recorded in the combined group.
Conclusion: Reported data in this study using the combination of ozone and steroid therapy could provide a new promising safe and effective adjunct therapy for management of OLP.
Keywords: Combined; Oral lichen planus; Ozone; Steroids.
Figures
References
-
- Scully C, Carrozzo M. Oral mucosal disease:lichen planus. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;46(1):15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjoms.2007.07.199 PMid:17822813. - PubMed
-
- Kini R, Nagaranta DV, Saha A. Therapeutic management of Oral Lichen Planus:a review for the clinicians. World J Dent. 2011;2(3):249–253. https://doi.org/10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1091.
-
- Basma Mostafa, Enji Ahmed. Prevalence of oral lichen planus among a sample of the Egyptian population. J Clin Exp Dent. 2015;7(1):e7–12. https://doi.org/10.4317/jced.51875 PMid:25810846 PMCid:PMC4368022. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gupta S, Ghosh S, Gupta S. Interventions for the management of oral lichen planus:a review of the conventional and novel therapies. Oral Diseases. 2017;23(8):1029–1042. https://doi.org/10.1111/odi.12634 PMid:28055124. - PubMed
-
- Sharma S, Saimbi CS, Koirala B. Erosive oral lichen planus and its management:A case series. Journal of the Nepal Medical Association. 2008;47(170):86–90. PMid:18709038. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources