Chitosan Microsphere Used as an Effective System to Deliver a Linked Antigenic Peptides Vaccine Protect Mice Against Acute and Chronic Toxoplasmosis
- PMID: 29876322
- PMCID: PMC5974094
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00163
Chitosan Microsphere Used as an Effective System to Deliver a Linked Antigenic Peptides Vaccine Protect Mice Against Acute and Chronic Toxoplasmosis
Abstract
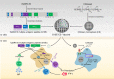
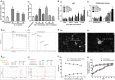
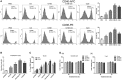
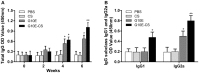
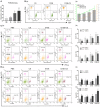
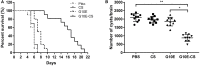
Multiple antigenic peptide (MAP) vaccines have advantages over traditional Toxoplasma gondii vaccines, but are more susceptible to enzymatic degradation. As an effective delivery system, chitosan microspheres (CS) can overcome this obstacle and act as a natural adjuvant to promote T helper 1 (Th1) cellular immune responses. In this study, we use chitosan microparticles to deliver multiple antigenic epitopes from GRA10 (G10E), containing three dominant epitopes. When G10E was entrapped within chitosan microparticles (G10E-CS), adequate peptides for eliciting immune response were loaded in the microsphere core and this complex released G10E peptides stably. The efficiency of G10E-CS was detected both in vitro, via cell culture, and through in vivo mouse immunization. In vitro, G10E-CS activated Dendritic Cells (DC) and T lymphocytes by upregulating the secretion of costimulatory molecules (CD40 and CD86). In vivo, Th1 biased cellular and humoral immune responses were activated in mice vaccinated with G10E-CS, accompanied by significantly increased production of IFN-γ, IL-2, and IgG, and decreases in IL-4, IL-10, and IgG1. Immunization with G10E-CS conferred significant protection with prolonged survival in mice model of acute toxoplasmosis and statistically significant decreases in cyst burden in murine chronic toxoplasmosis. The results from this study indicate that chitosan microspheres used as an effective system to deliver a linked antigenic peptides is a promising strategy for the development of efficient vaccine against T. gondii.
Keywords: Toxoplasma gondii; chitosan microspheres; epitopes; peptides; vaccine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Designing a multi-epitope vaccine using Toxoplasma ROP5, ROP7, and SAG1 epitopes and immunogenicity evaluation against acute and chronic toxoplasmosis in BABL/c mice.Microb Pathog. 2025 Jul;204:107567. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2025.107567. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Microb Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40216097
-
Toxoplasma gondii: Vaccination with a DNA vaccine encoding T- and B-cell epitopes of SAG1, GRA2, GRA7 and ROP16 elicits protection against acute toxoplasmosis in mice.Vaccine. 2015 Nov 27;33(48):6757-62. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.10.077. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 26518401
-
Plant Hsp90 is a novel adjuvant that elicits a strong humoral and cellular immune response against B- and T-cell epitopes of a Toxoplasma gondii SAG1 peptide.Parasit Vectors. 2019 Mar 25;12(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3362-6. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 30909938 Free PMC article.
-
Candidate antigenic epitopes for vaccination and diagnosis strategies of Toxoplasma gondii infection: A review.Microb Pathog. 2019 Dec;137:103788. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103788. Epub 2019 Oct 9. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31605758 Review.
-
Vaccines in Congenital Toxoplasmosis: Advances and Perspectives.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 15;11:621997. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.621997. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33658997 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protective efficacy of Toxoplasma gondii GRA12 or GRA7 recombinant proteins encapsulated in PLGA nanoparticles against acute Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Jul 12;13:1209755. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1209755. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37502604 Free PMC article.
-
Immunization with a novel mRNA vaccine, TGGT1_216200 mRNA-LNP, prolongs survival time in BALB/c mice against acute toxoplasmosis.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 14;14:1161507. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1161507. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37122740 Free PMC article.
-
High-performance lung-targeted bio-responsive platform for severe colistin-resistant bacterial pneumonia therapy.Bioact Mater. 2024 Feb 21;35:517-533. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.02.017. eCollection 2024 May. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 38404643 Free PMC article.
-
Immunization with plasmid DNA expressing Heat Shock Protein 40 confers prophylactic protection against chronic Toxoplasma gondii infection in Kunming mice.Parasite. 2018;25:37. doi: 10.1051/parasite/2018040. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Parasite. 2018. PMID: 30040611 Free PMC article.
-
A multiepitope vaccine encoding four Eimeria epitopes with PLGA nanospheres: a novel vaccine candidate against coccidiosis in laying chickens.Vet Res. 2022 Apr 1;53(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13567-022-01045-w. Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35365221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bastos L. M., Macêdo A. G., Silva M. V., Santiago F. M., Ramos E. L., Santos F. A., et al. . (2016). Toxoplasma gondii-derived synthetic peptides containing B- and T-cell epitopes from Gra2 protein are able to enhance mice survival in a model of experimental toxoplasmosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 6:59. 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00059 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

