Rational Design and Evaluation of an Artificial Escherichia coli K1 Protein Vaccine Candidate Based on the Structure of OmpA
- PMID: 29876324
- PMCID: PMC5974202
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00172
Rational Design and Evaluation of an Artificial Escherichia coli K1 Protein Vaccine Candidate Based on the Structure of OmpA
Abstract
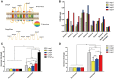
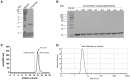
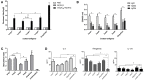
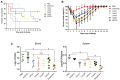
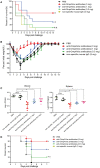
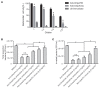
Escherichia coli (E. coli) K1 causes meningitis and remains an unsolved problem in neonates, despite the application of antibiotics and supportive care. The cross-reactivity of bacterial capsular polysaccharides with human antigens hinders their application as vaccine candidates. Thus, protein antigens could be an alternative strategy for the development of an E. coli K1 vaccine. Outer membrane protein A (OmpA) of E. coli K1 is a potential vaccine candidate because of its predominant contribution to bacterial pathogenesis and sub-cellular localization. However, little progress has been made regarding the use of OmpA for this purpose due to difficulties in OmpA production. In the present study, we first investigated the immunogenicity of the four extracellular loops of OmpA. Using the structure of OmpA, we rationally designed and successfully generated the artificial protein OmpAVac, composed of connected loops from OmpA. Recombinant OmpAVac was successfully produced in E. coli BL21 and behaved as a soluble homogenous monomer in the aqueous phase. Vaccination with OmpAVac induced Th1, Th2, and Th17 immune responses and conferred effective protection in mice. In addition, OmpAVac-specific antibodies were able to mediate opsonophagocytosis and inhibit bacterial invasion, thereby conferring prophylactic protection in E. coli K1-challenged adult mice and neonatal mice. These results suggest that OmpAVac could be a good vaccine candidate for the control of E. coli K1 infection and provide an additional example of structure-based vaccine design.
Keywords: Escherichia coli K1; extracellular loops; meningitis; outer membrane protein A; structure-based vaccine design.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recombinant outer membrane protein A induces a protective immune response against Escherichia coli infection in mice.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Jul;99(13):5451-60. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-6339-6. Epub 2015 Jan 8. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25567514
-
Antigenic epitopes on the outer membrane protein A of Escherichia coli identified with single-chain variable fragment (scFv) antibodies.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Jul;103(13):5285-5299. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09761-8. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31028439
-
Recombinant outer membrane protein A fragments protect against Escherichia coli meningitis.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2016 Jun;49(3):329-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2014.07.012. Epub 2014 Oct 8. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2016. PMID: 25305709
-
Advances in vaccination against avian pathogenic Escherichia coli respiratory disease: potentials and limitations.Vet Microbiol. 2014 Aug 6;172(1-2):13-22. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.04.019. Epub 2014 May 5. Vet Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24878325 Review.
-
Neonatal meningitis due of Escherichia coli K1.J Infect Dis. 1977 Aug;136 Suppl:S93-7. doi: 10.1093/infdis/136.supplement.s93. J Infect Dis. 1977. PMID: 330780 Review.
Cited by
-
Outer Membrane Protein of Gut Commensal Microorganism Induces Autoantibody Production and Extra-Intestinal Gland Inflammation in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 19;19(10):3241. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103241. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30347705 Free PMC article.
-
Human Monoclonal Antibodies to Escherichia coli Outer Membrane Protein A Porin Domain Cause Aggregation but Do Not Alter In Vivo Bacterial Burdens in a Murine Sepsis Model.Infect Immun. 2022 Jun 16;90(6):e0017622. doi: 10.1128/iai.00176-22. Epub 2022 May 18. Infect Immun. 2022. PMID: 35583347 Free PMC article.
-
The Potentials of Melatonin in the Prevention and Treatment of Bacterial Meningitis Disease.Molecules. 2021 Mar 5;26(5):1419. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051419. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33808027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Bioinformatic Assessments of the Variability of Neisseria gonorrhoeae Vaccine Candidates.mSphere. 2021 Feb 3;6(1):e00977-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00977-20. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 33536323 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccines against extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC): progress and challenges.Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2359691. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2359691. Epub 2024 Jun 2. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 38825856 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cierpicki T., Liang B., Tamm L. K., Bushweller J. H. (2006). Increasing the accuracy of solution NMR structures of membrane proteins by application of residual dipolar couplings. High-resolution structure of outer membrane protein A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 6947–6951. 10.1021/ja0608343 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

