Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Familial Hypercholesterolemia 2017
- PMID: 29877295
- PMCID: PMC6099072
- DOI: 10.5551/jat.CR003
Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Familial Hypercholesterolemia 2017
Abstract
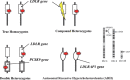
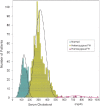
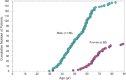
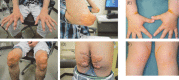
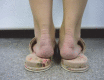
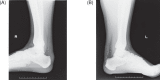
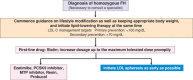
Statement1. Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is an autosomal hereditary disease with the 3 major clinical features of hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia, premature coronary artery disease and tendon and skin xanthomas. As there is a considerably high risk of coronary artery disease (CAD), in addition to early diagnosis and intensive treatment, family screening (cascade screening) is required (Recommendation level A) 2. For a diagnosis of FH, at least 2 of the following criteria should be satisfied:① LDL-C ≥180 mg/dL, ② Tendon/skin xanthomas, ③ History of FH or premature CAD within 2nd degree blood relatives (Recommendation level A) 3. Intensive lipid-lowering therapy is necessary for the treatment of FH. First-line drug should be statins. (Recommendation level A, Evidence level 3) 4. Screening for CAD as well as asymptomatic atherosclerosis should be conducted periodically in FH patients. (Recommendation level A) 5. For homozygous FH, consider LDL apheresis and treatment with PCSK9 inhibitors or MTP inhibitors. (Recommendation level A) 6. For severe forms of heterozygous FH who have resistant to drug therapy, consider PCSK9 inhibitors and LDL apheresis. (Recommendation level A) 7. Refer FH homozygotes as well as heterozygotes who are resistant to drug therapy, who are children or are pregnant or have the desire to bear children to a specialist. (Recommendation level A).
Keywords: Adult; Diagnosis criteria; Drug therapy; Familial hypercholesterolemia; Heterozygote; Homozygote; LDL apheresis; Lifestyle habits; Treatment guidelines.
Conflict of interest statement
Honoraria: Yokote K; Astellas Pharma Inc., Astra-Zeneca K.K., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited., MSD K.K., Kowa Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Kowa Company, Ltd., Taisho Toyama Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited, Pfizer Japan Inc., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd., Sanwa Kagaku Kenkyusho Co., Ltd., Mochida Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd.. Arai H; Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited, MSD K.K., Abbott Jpn Co., Ltd., Astellas Pharma Inc., Kowa Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Amgen Astellas BioPharma K.K., Sanofi K.K.. Yamashita S; Kowa Company, Ltd., MSD K.K./Merck & Co, Bayer Yakuhin, Ltd, Kowa Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Skylight Biotech, Inc., Amgen Astellas BioPharma K.K., Pfizer Japan Inc., Dai Nippon Printing Co., Ltd., Sanwa Kagaku Kenkyusho Co., Ltd., Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited., Bayer Yakuhin, Ltd. Harada-Shiba M; Kowa Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Pfizer Japan Inc., Astellas Pharma Inc., Amgen Astellas Bio-Pharma K.K., Sanofi K.K.. Ishigaki Y; MSD K.K., Astellas Pharma Inc., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Sanofi K.K., Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, AstraZeneca K.K., Kowa Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.. Ishibashi S; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited., Kowa Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., MSD K.K., Sanwa Kagaku Kenkyusho Co., Ltd., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, AstraZeneca K.K.. Nohara A; Amgen Astellas BioPharma K.K., Astellas Pharma Inc., Sanofi K.K.. Miyauchi K; Amgen Astellas BioPharma K.K., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited., Nippon Boehringer In gelheim Co., Sanofi K.K., MSD K.K., Bayer Yakuhin, Ltd, Astellas Pharma Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited. Fees for promotional materials: Yama shita S; Shionogi & Co., Ltd.. Research funding: Yokote K; Astellas Pharma Inc.. Arai H; Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.. Yamashita S; Kowa Company, Ltd., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Bayer Yakuhin, Ltd, Kyowa Medex Co., Ltd., National Institutes of Biomedical Innovation, Health and Nutrition., Sanwa Kagaku Kenkyusho Co., Ltd., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Kowa Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.. Harada-Shiba M; PPD-SNBL K.K.. Ogura M; Sappro Holdings Ltd.. Research funding: Yokote K; Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited., Bristol-Myers Squibb, Astellas Pharma Inc., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Taisho Toyama Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., MSD K.K., Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd., Pfizer Japan Inc., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Teijin Pharma Limited., Mochida Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Toyama Chemical Co., Ltd., Kowa Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., AstraZeneca K.K., Sanofi K.K., Eisai Co., Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K., Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.. Arai H; Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited, Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.. Yama shita S; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited., Astellas Pharma Inc., Sanwa Kagaku Kenkyusho Co., Ltd., MSD K.K., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., AstraZeneca K.K., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Mochida Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.. Harada-Shiba M; Astellas Pharma Inc., Kaneka Medix Corp. Ishigaki Y; MSD K.K., Kowa Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited.. Ishibashi S; Astellas Pharma Inc., Taisho Toyama Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Sanofi K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Daiichi Sankyo Company, Limited, Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Kowa Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd.. Nohara A; Sanofi K.K., MSD K.K., Aegerion Pharmaceuticals, Inc.. Research funding Others: Nohara A; Sanofi K.K., MSD K.K., Keiai-Kai Medical Corp., Shionogi & Co. Ltd., Kowa Co. Ltd., Astellas Pharma Inc., AstraZeneca, Biopharm of Japan Corp., Kaneka Medix Corp., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.. Yokote K; MSD K.K.. Yamashita S; Rinku General Medical Center, Izumisano City, Kaizuka City Hospital, Kaizuka City.
Figures


References
-
- Mabuchi H, Koizumi J, Shimizu M, Takeda R: Development of coronary heart disease in familial hypercholesterolemia. Circulation, 1989; 79: 225-232 - PubMed
-
- Nordestgaard BG, Chapman MJ, Humphries SE, Ginsberg HN, Masana L, Descamps OS, Wiklund O, Hegele RA, Raal FJ, Defesche JC, Wiegman A, Santos RD, Watts GF, Parhofer KG, Hovingh GK, Kovanen PT, Boileau C, Averna M, Boren J, Bruckert E, Catapano AL, Kuivenhoven JA, Pajukanta P, Ray K, Stalenhoef AF, Stroes E, Taskinen MR, Tybjaerg-Hansen A: Familial hypercholesterolaemia is underdiagnosed and undertreated in the general population: guidance for clinicians to prevent coronary heart disease: Consensus Statement of the European Atherosclerosis Society. Eur Heart J, 2013; 34: 3478-3490 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ohta N, Hori M, Takahashi A, Ogura M, Makino H, Tamanaha T, Fujiyama H, Miyamoto Y, Harada-Shiba M: Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 9 V4I variant with LDLR mutations modifies the phenotype of familial hypercholesterolemia. J Clin Lipidol, 2015; 10: 547-555 e545 - PubMed
-
- Mabuchi H, Nohara A, Noguchi T, Kobayashi J, Kawashiri MA, Tada H, Nakanishi C, Mori M, Yamagishi M, Inazu A, Koizumi J: Molecular genetic epidemiology of homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia in the Hokuriku district of Japan. Atherosclerosis, 2011; 214: 404-407 - PubMed
-
- Abifadel M, Varret M, Rabes JP, Allard D, Ouguerram K, Devillers M, Cruaud C, Benjannet S, Wickham L, Erlich D, Derre A, Villeger L, Farnier M, Beucler I, Bruckert E, Chambaz J, Chanu B, Lecerf JM, Luc G, Moulin P, Weissenbach J, Prat A, Krempf M, Junien C, Seidah NG, Boileau C: Mutations in PCSK9 cause autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Nat Genet, 2003; 34: 154-156 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

