miRNAS in cardiovascular diseases: potential biomarkers, therapeutic targets and challenges
- PMID: 29877320
- PMCID: PMC6289363
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2018.30
miRNAS in cardiovascular diseases: potential biomarkers, therapeutic targets and challenges
Abstract
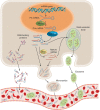
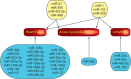
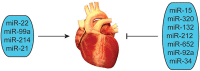
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in the world. Although considerable progress has been made in the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of CVD, there is still a critical need for novel diagnostic biomarkers and new therapeutic interventions to decrease the incidence of this disease. Recently, there is increasing evidence that circulating miRNAs (miRNAs), i.e. endogenous, stable, single-stranded, short, non-coding RNAs, can be used as diagnostic biomarkers for CVD. Furthermore, miRNAs represent potential novel therapeutic targets for several cardiovascular disorders. In this review we provides an overview of the effects of several CVD; including heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, arrhythmias and pulmonary hypertension; on levels of circulating miRNAs. In addition, the use of miRNA as therapeutic targets is also discussed, as well as challenges and recommendations in their use in the diagnosis of CVD.
Keywords: biomarker; cardiovascular diseases; microRNA; therapeutic targets.
Figures
References
-
- Gupta SK, Foinquinos A, Thum S, Remke J, Zimmer K, Bauters C, et al. Preclinical development of a microRNA-based therapy for elderly patients with myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68:1557–71. - PubMed
-
- Marques FZ, Campain AE, Tomaszewski M, Zukowska-Szczechowska E, Yang YH, Charchar FJ, et al. Gene expression profiling reveals renin mRNA overexpression in human hypertensive kidneys and a role for microRNAs. Hypertension. 2011;58:1093–8. - PubMed
-
- Barwari T, Joshi A, Mayr M. MicroRNAs in cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68:2577–84. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The c-elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

