Quality indicators for responsible antibiotic use in the inpatient setting: a systematic review followed by an international multidisciplinary consensus procedure
- PMID: 29878221
- PMCID: PMC5989598
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dky116
Quality indicators for responsible antibiotic use in the inpatient setting: a systematic review followed by an international multidisciplinary consensus procedure
Abstract
Background: This study was conducted as part of the Driving Reinvestment in Research and Development and Responsible Antibiotic Use (DRIVE-AB) project and aimed to develop generic quality indicators (QIs) for responsible antibiotic use in the inpatient setting.
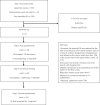
Methods: A RAND-modified Delphi method was applied. First, QIs were identified by a systematic review. A complementary search was performed on web sites of relevant organizations. Duplicates were removed and disease and patient-specific QIs were combined into generic indicators. The relevance of these QIs was appraised by a multidisciplinary international stakeholder panel through two questionnaires and an in-between consensus meeting.
Results: The systematic review retrieved 70 potential generic QIs. The QIs were appraised by 25 international stakeholders with diverse backgrounds (medical community, public health, patients, antibiotic research and development, regulators, governments). Ultimately, 51 QIs were selected in consensus. QIs with the highest relevance score included: (i) an antibiotic plan should be documented in the medical record at the start of the antibiotic treatment; (ii) the results of bacteriological susceptibility testing should be documented in the medical record; (iii) the local guidelines should correspond to the national guidelines but should be adapted based on local resistance patterns; (iv) an antibiotic stewardship programme should be in place at the healthcare facility; and (v) allergy status should be taken into account when antibiotics are prescribed.
Conclusions: This systematic and stepwise method combining evidence from literature and stakeholder opinion led to multidisciplinary international consensus on generic inpatient QIs that can be used globally to assess the quality of antibiotic use.
Figures
References
-
- Laxminarayan R, Duse A, Wattal C. et al. Antibiotic resistance—the need for global solutions. Lancet Infect Dis 2013; 13: 1057–98. - PubMed
-
- de Kraker ME, Wolkewitz M, Davey PG. et al. Burden of antimicrobial resistance in European hospitals: excess mortality and length of hospital stay associated with bloodstream infections due to Escherichia coli resistant to third-generation cephalosporins. J Antimicrob Chemother 2011; 66: 398–407. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. The Evolving Threat of Antimicrobial Resistance: Options for Action http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/44812/1/9789241503181_eng.pdf.
-
- Shlaes DM, Gerding DN, John JF. et al. Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America and Infectious Diseases Society of America Joint Committee on the Prevention of Antimicrobial Resistance: guidelines for the prevention of antimicrobial resistance in hospitals. Clin Infect Dis 1997; 25: 584–99. - PubMed
-
- Report from the Invitational EU Conference on the Microbial Threat: The Copenhagen Recommendations. http://soapimg.icecube.snowfall.se/strama/Kopenhamnsmotet_1998.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical