The conserved LEM-3/Ankle1 nuclease is involved in the combinatorial regulation of meiotic recombination repair and chromosome segregation in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 29879106
- PMCID: PMC6007928
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007453
The conserved LEM-3/Ankle1 nuclease is involved in the combinatorial regulation of meiotic recombination repair and chromosome segregation in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
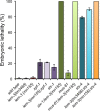
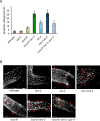
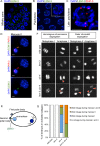
Homologous recombination is essential for crossover (CO) formation and accurate chromosome segregation during meiosis. It is of considerable importance to work out how recombination intermediates are processed, leading to CO and non-crossover (NCO) outcome. Genetic analysis in budding yeast and Caenorhabditis elegans indicates that the processing of meiotic recombination intermediates involves a combination of nucleases and DNA repair enzymes. We previously reported that in C. elegans meiotic joint molecule resolution is mediated by two redundant pathways, conferred by the SLX-1 and MUS-81 nucleases, and by the HIM-6 Bloom helicase in conjunction with the XPF-1 endonuclease, respectively. Both pathways require the scaffold protein SLX-4. However, in the absence of all these enzymes, residual processing of meiotic recombination intermediates still occurs and CO formation is reduced but not abolished. Here we show that the LEM-3 nuclease, mutation of which by itself does not have an overt meiotic phenotype, genetically interacts with slx-1 and mus-81 mutants, the respective double mutants displaying 100% embryonic lethality. The combined loss of LEM-3 and MUS-81 leads to altered processing of recombination intermediates, a delayed disassembly of foci associated with CO designated sites, and the formation of univalents linked by SPO-11 dependent chromatin bridges (dissociated bivalents). However, LEM-3 foci do not colocalize with ZHP-3, a marker that congresses into CO designated sites. In addition, neither CO frequency nor distribution is altered in lem-3 single mutants or in combination with mus-81 or slx-4 mutations. Finally, we found persistent chromatin bridges during meiotic divisions in lem-3; slx-4 double mutants. Supported by the localization of LEM-3 between dividing meiotic nuclei, this data suggest that LEM-3 is able to process erroneous recombination intermediates that persist into the second meiotic division.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Kohl KP, Sekelsky J. Meiotic and mitotic recombination in meiosis. Genetics. 2013;194(2):327–34. Epub 2013/06/05. doi: 10.1534/genetics.113.150581 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3664844. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Keeney S. Spo11 and the formation of DNA double-strand breaks in meiosis. Genome Dyn Stab. 2008;2:81–123. Epub 2008/01/01. doi: 10.1007/7050_2007_026 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3172816. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buhler C, Borde V, Lichten M. Mapping meiotic single-strand DNA reveals a new landscape of DNA double-strand breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS Biol. 2007;5(12):e324 Epub 2007/12/14. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060104 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2121111. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moens PB, Kolas NK, Tarsounas M, Marcon E, Cohen PE, Spyropoulos B. The time course and chromosomal localization of recombination-related proteins at meiosis in the mouse are compatible with models that can resolve the early DNA-DNA interactions without reciprocal recombination. J Cell Sci. 2002;115(Pt 8):1611–22. Epub 2002/04/16. . - PubMed
-
- Rosu S, Libuda DE, Villeneuve AM. Robust crossover assurance and regulated interhomolog access maintain meiotic crossover number. Science. 2011;334(6060):1286–9. Epub 2011/12/07. doi: 10.1126/science.1212424 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3360972. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

