Incidence of Fellow Eye Involvement in Patients With Unilateral Exudative Age-Related Macular Degeneration
- PMID: 29879284
- PMCID: PMC6142947
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2018.2154
Incidence of Fellow Eye Involvement in Patients With Unilateral Exudative Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Abstract
Importance: Since the advent of optical coherence tomography angiography (OCT-A), nonexudative neovascularization has been described in the fellow eyes of unilateral exudative age-related macular degeneration (AMD). However, there is limited literature describing the natural course and optimal management of these lesions.
Objective: To determine the incidence of fellow eye involvement in patients presenting with unilateral typical AMD or polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy and to evaluate the patterns of OCT-A changes within 6 months before the onset of exudative changes, especially focusing on nonexudative neovascularization.
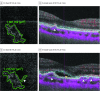
Design, setting, and participants: Data for this study were taken from a prospective, observational cohort study involving Asian patients with exudative AMD in the Asian AMD Phenotyping Study between October 2015 and March 2016. Analyses began in June 2017. Only patients who had gradable OCT-A and indocyanine green angiography (ICGA) scans of the fellow eye at baseline and follow-up at least 6 months apart were included for the analysis. The contralateral eye was evaluated for presence of nonexudative neovascularization based on multimodal imaging, which included ICGA, spectral domain optical coherence tomography, and OCT-A.
Main outcomes and measures: The difference between the incidence of those with nonexudative choroidal neovascularization and those without as analyzed using log-rank test and qualitative analysis of OCT-A images.
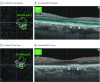
Results: We included 95 fellow eyes of 95 patients who presented with unilateral exudative AMD with a mean (SD) age of 68.6 (8.6) years. Nonexudative neovascularization was present in 18 eyes (19%) (8 [22.9%] and 10 [19.0%] fellow eyes with typical AMD and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy, respectively; 8 [44.4%] on OCT-A; 5 [27.8%] on ICGA; and 5 [27.8%] on both OCT-A and ICGA). Development of exudative changes was noted in 6 fellow eyes (6.3%). Four eyes developed exudation from previously noted nonexudative neovascularization, and 2 eyes arose exudative changes from de novo. The probability of developing exudation within 6 months was significantly higher in eyes with baseline nonexudative neovascularization (0.087; 95% CI, 0.0033-0.210) compared with eyes without (0.010; 95% CI, 0.0026-0.041) (P = .008). In all eyes whose OCT-A images were available immediately before the onset of exudative changes, there was an increase in the size of network vessels compared with baseline.
Conclusions and relevance: The presence of nonexudative neovascularization may predispose to the development of exudative changes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Wong WL, Su X, Li X, et al. . Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2(2):e106-e116. - PubMed
-
- Lim LS, Mitchell P, Seddon JM, Holz FG, Wong TY. Age-related macular degeneration. Lancet. 2012;379(9827):1728-1738. - PubMed
-
- Green WR, McDonnell PJ, Yeo JH. Pathologic features of senile macular degeneration. Ophthalmology. 1985;92(5):615-627. - PubMed
-
- Spraul CW, Grossniklaus HE. Characteristics of Drusen and Bruch’s membrane in postmortem eyes with age-related macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997;115(2):267-273. - PubMed
-
- Bottoni FG, Aandekerk AL, Deutman AF. Clinical application of digital indocyanine green videoangiography in senile macular degeneration. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1994;232(8):458-468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

