Neuroimaging Impaired Response Inhibition and Salience Attribution in Human Drug Addiction: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 29879391
- PMCID: PMC5995133
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.03.048
Neuroimaging Impaired Response Inhibition and Salience Attribution in Human Drug Addiction: A Systematic Review
Abstract
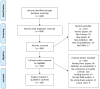
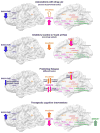
The impaired response inhibition and salience attribution (iRISA) model proposes that impaired response inhibition and salience attribution underlie drug seeking and taking. To update this model, we systematically reviewed 105 task-related neuroimaging studies (n > 15/group) published since 2010. Results demonstrate specific impairments within six large-scale brain networks (reward, habit, salience, executive, memory, and self-directed networks) during drug cue exposure, decision making, inhibitory control, and social-emotional processing. Addicted individuals demonstrated increased recruitment of these networks during drug-related processing but a blunted response during non-drug-related processing, with the same networks also being implicated during resting state. Associations with real-life drug use, relapse, therapeutic interventions, and the relevance to initiation of drug use during adolescence support the clinical relevance of the results. Whereas the salience and executive networks showed impairments throughout the addiction cycle, the reward network was dysregulated at later stages of abuse. Effects were similar in alcohol, cannabis, and stimulant addiction.
Keywords: cocaine; craving; dependence; fMRI; heroin; marijuana; nicotine; opioid; smoking; youth.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
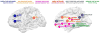



References
-
- Albein-Urios N, Verdejo-Román J, Asensio S, Soriano-Mas C, Martínez-González JM, Verdejo-García A. Re-appraisal of negative emotions in cocaine dependence: Dysfunctional corticolimbic activation and connectivity. Addict Biol. 2012;19:415–426. - PubMed
-
- Aron AR, Robbins TW, Poldrack Ra. Inhibition and the right inferior frontal cortex: one decade on. Trends Cogn Sci. 2014;18:177–185. - PubMed
-
- Asensio S, Romero MJ, Palau C, Sanchez A, Senabre I, Morales JL, Carcelen R, Romero FJ. Altered neural response of the appetitive emotional system in cocaine addiction: An fMRI Study. Addict Biol. 2010;15:504–516. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

