Importance of kynurenine 3-monooxygenase for spontaneous firing and pharmacological responses of midbrain dopamine neurons: Relevance for schizophrenia
- PMID: 29879409
- PMCID: PMC6794148
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.06.003
Importance of kynurenine 3-monooxygenase for spontaneous firing and pharmacological responses of midbrain dopamine neurons: Relevance for schizophrenia
Abstract
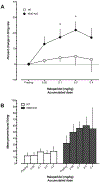
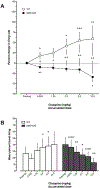
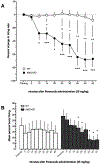
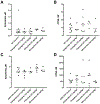
Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase (KMO) is an essential enzyme of the kynurenine pathway, converting kynurenine into 3-hydroxykynurenine. Inhibition of KMO increases kynurenine, resulting in elevated levels of kynurenic acid (KYNA), an endogenous N-methyl-d-aspartate and α*7-nicotinic receptor antagonist. The concentration of KYNA is elevated in the brain of patients with schizophrenia, possibly as a result of a reduced KMO activity. In the present study, using in vivo single cell recording techniques, we investigated the electrophysiological characteristics of ventral tegmental area dopamine (VTA DA) neurons and their response to antipsychotic drugs in a KMO knock-out (K/O) mouse model. KMO K/O mice exhibited a marked increase in spontaneous VTA DA neuron activity as compared to wild-type (WT) mice. Furthermore, VTA DA neurons showed clear-cut, yet qualitatively opposite, responses to the antipsychotic drugs haloperidol and clozapine in the two genotypes. The anti-inflammatory drug parecoxib successfully lowered the firing activity of VTA DA neurons in KMO K/O, but not in WT mice. Minocycline, an antibiotic and anti-inflammatory drug, produced no effect in this regard. Taken together, the present data further support the usefulness of KMO K/O mice for studying distinct aspects of the pathophysiology and pharmacological treatment of psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia.
Keywords: Dopamine; Electrophysiology; Kynurenic acid; NMDA receptor; Schizophrenia.
Copyright © 2018. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of interest
None.
Figures
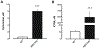
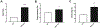
References
-
- Aoyama N, Takahashi N, Saito S, Maeno N, Ishihara R, Ji X, Miura H, Ikeda M, Suzuki T, Kitajima T, Yamanouchi Y, Kinoshita Y, Yoshida K, Iwata N, Inada T, Ozaki N, 2006. Association study between kynurenine 3-monooxygenase gene and schizophrenia in the Japanese population. Gene Brain Behav 5, 364–368. 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2006.00231.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Basu GD, Tinder TL, Bradley JM, Tu T, Hattrup CL, Pockaj BA, Mukherjee P, 2006. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor enhances the efficacy of a breast cancer vaccine: role of Ido. J. Immunol 177, 2391–2402. - PubMed
-
- Billups D, Attwell D, 2003. Active release of glycine or D-serine saturates the glycine site of NMDA receptors at the cerebellar mossy fibre to granule cell synapse. Eur. J. Neurosci 18, 2975–2980. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

