Re-Evaluating E-Cadherin and β-Catenin: A Pan-Cancer Proteomic Approach with an Emphasis on Breast Cancer
- PMID: 29879416
- PMCID: PMC6119824
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.05.003
Re-Evaluating E-Cadherin and β-Catenin: A Pan-Cancer Proteomic Approach with an Emphasis on Breast Cancer
Abstract
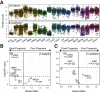
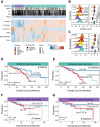
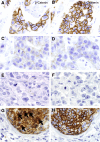
E-cadherin is conventionally considered to be a good prognostic marker in cancer. The loss of E-cadherin is one of the key hallmarks of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, a biological process that promotes cancer cell invasiveness and metastasis. Recent evidence has cast doubt on the importance of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in metastasis. The availability of protein-level data in the Cancer Genome Atlas allows for the quantitative analysis of protein and prognosis. The prognostic values of E-cadherin and β-catenin were revisited across 19 cancer types, and high E-cadherin was found to correlate with good prognosis in most cancers. Conversely, higher E-cadherin and β-catenin correlated with shorter survival in invasive breast carcinoma. Stratifying breast cancers by histologic subtype revealed that the poor prognosis of E-cadherin and β-catenin proteins was characteristic of infiltrating ductal, but not lobular, carcinomas. To further corroborate the protein findings and examine cellular localization, immunohistochemistry was used for E-cadherin and β-catenin in 163 breast patient samples from the Iowa cohort. Most previous studies showing that reduced or absent E-cadherin and β-catenin was inversely associated with tumor stages in ductal carcinomas were confirmed. Taken together, these results lead us to question the prognostic values of E-cadherin and β-catenin in ductal carcinomas and indicate a complicated role of E-cadherin and β-catenin in breast cancer progression.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic values of osteopontin-c, E-cadherin and β-catenin in breast cancer.Cancer Epidemiol. 2013 Dec;37(6):985-92. doi: 10.1016/j.canep.2013.08.005. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Cancer Epidemiol. 2013. PMID: 24012693 Clinical Trial.
-
Expression of adhesion proteins E-cadherin, alpha-catenin, beta-catenin and gamma-catenin is different in T1 and T2 breast tumours.Pathology. 2006 Oct;38(5):403-7. doi: 10.1080/00313020600922520. Pathology. 2006. PMID: 17008277
-
Simultaneous loss of E-cadherin and catenins in invasive lobular breast cancer and lobular carcinoma in situ.J Pathol. 1997 Dec;183(4):404-11. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199712)183:4<404::AID-PATH1148>3.0.CO;2-9. J Pathol. 1997. PMID: 9496256
-
E-cadherin staining in the diagnosis of lobular versus ductal neoplasms of the breast: the emperor has no clothes.Histopathology. 2025 Feb;86(3):327-340. doi: 10.1111/his.15295. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Histopathology. 2025. PMID: 39138705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lobular neoplasia of the breast revisited with emphasis on the role of E-cadherin immunohistochemistry.Am J Surg Pathol. 2013 Jul;37(7):e1-11. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182918a2b. Am J Surg Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23759937 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-205-5p Downregulation and ZEB1 Upregulation Characterize the Disseminated Tumor Cells in Patients with Invasive Ductal Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 22;23(1):103. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010103. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008529 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition on the Immune Landscape in Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 12;13(20):5099. doi: 10.3390/cancers13205099. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680248 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome derangement in malignant epithelial cells and its stroma following exposure to 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone.Arch Toxicol. 2023 Mar;97(3):711-720. doi: 10.1007/s00204-022-03426-8. Epub 2022 Nov 25. Arch Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 36434399 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of triple negative breast cancer-associated inflammation, tumor growth and brain colonization by targeting monoacylglycerol lipase.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 29;12(1):5328. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09358-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35351947 Free PMC article.
-
Multiomics insights on the onset, progression, and metastatic evolution of breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Dec 19;13:1292046. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1292046. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38169859 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mayer B., Johnson J.P., Leitl F., Jauch K.W., Heiss M.M., Schildberg F.W., Birchmeier W., Funke I. E-cadherin expression in primary and metastatic gastric cancer: down-regulation correlates with cellular dedifferentiation and glandular disintegration. Cancer Res. 1993;53:1690–1695. - PubMed
-
- Bremnes R.M., Veve R., Hirsch F.R., Franklin W.A. The E-cadherin cell-cell adhesion complex and lung cancer invasion, metastasis, and prognosis. Lung Cancer. 2002;36:115–124. - PubMed
-
- Bringuier P.P., Umbas R., Schaafsma H.E., Karthaus H.F., Debruyne F.M., Schalken J.A. Decreased E-cadherin immunoreactivity correlates with poor survival in patients with bladder tumors. Cancer Res. 1993;53:3241–3245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

