Plasma Galectin-3 and Sonographic Measures of Carotid Atherosclerosis in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study
- PMID: 29879846
- PMCID: PMC6239970
- DOI: 10.1177/0003319718780772
Plasma Galectin-3 and Sonographic Measures of Carotid Atherosclerosis in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study
Abstract
Galectin-3 is a β-galactoside-binding lectin that plays a role in the regulation of several conditions that are associated with atherosclerosis. The goal of this cross-sectional study was to assess the association of plasma galectin-3 concentrations with sonographic measures of carotid atherosclerosis in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study. Linear regression was used to determine the difference and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) by categorical and continuous representations of galectin-3. Logistic regression was used to determine the odds ratio and 95% CI, separately, for dichotomized cIMT (75th percentile = 0.9 mm) and carotid plaque and/or shadowing. Compared to those in the first quintile of galectin-3, those in the fifth quintile of galectin-3 level had higher cIMT (mean difference: 0.020 mm after multivariable adjustment; P trend = .04). Moreover, compared to those in the lowest galectin-3 quintile, those in the highest galectin-3 quintile had higher odds of carotid plaque/and or shadowing (odds ratio 1.13 after multivariable adjustment; P trend = .014). Higher levels of galectin-3 are associated with greater carotid atherosclerosis. Our findings provide support for the role of inflammatory biomarkers in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and suggest galectin-3 as a possible target for intervention in the prevention or management of atherosclerotic disease.
Keywords: ARIC; atherosclerosis; carotid intima–media thickness; galectin-3; plaque; shadowing.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
Financial disclosure for Christie M. Ballantyne, MD:
Grant/research support: Abbott Diagnostics, Roche Diagnostics (to institution, not individual).
Consultant: Abbott Diagnostics, Roche Diagnostics.
Patent pending: Provisional patent (patent no. 61721475) entitled “Biomarkers to Improve Prediction of Heart Failure Risk” filed by Baylor College of Medicine and Roche.
The other co-authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
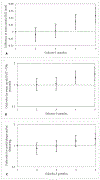
Comment in
-
Galectin-3: An Early Marker of Gestational Diabetes, Subclinical Atherosclerosis, and Tumor Progression.Angiology. 2020 May;71(5):474. doi: 10.1177/0003319719831870. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Angiology. 2020. PMID: 30791704 No abstract available.
-
Galectin-3: A New Biomarker for Atherosclerosis Management.Angiology. 2020 Nov;71(10):966. doi: 10.1177/0003319720941763. Epub 2020 Jul 17. Angiology. 2020. PMID: 32677461 No abstract available.
References
-
- Roquer J, Ois A. Atherosclerotic Burden and Mortality In: Preedy VR, Watson RR, editors. Handbook of Disease Burdens and Quality of Life Measures. New York, NY: Springer New York; 2010, p. 899–918.
-
- Barquera S, Pedroza-Tobias A, Medina C, et al. Global overview of the epidemiology of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Arch Med Res. 2015;46;328–38. - PubMed
-
- Falk E Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47(8 Suppl):C7–12. - PubMed
-
- Hansson GK, Hermansson A. The immune system in atherosclerosis. Nat Immunol. 2011;12:204–12. - PubMed
-
- Ross R. Atherosclerosis — An inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:115–26. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

