Clay mineral diversity and abundance in sedimentary rocks of Gale crater, Mars
- PMID: 29881776
- PMCID: PMC5990309
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aar3330
Clay mineral diversity and abundance in sedimentary rocks of Gale crater, Mars
Abstract
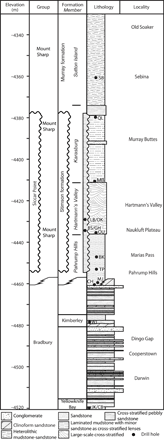
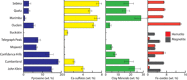
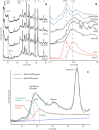
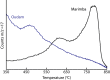
Clay minerals provide indicators of the evolution of aqueous conditions and possible habitats for life on ancient Mars. Analyses by the Mars Science Laboratory rover Curiosity show that ~3.5-billion year (Ga) fluvio-lacustrine mudstones in Gale crater contain up to ~28 weight % (wt %) clay minerals. We demonstrate that the species of clay minerals deduced from x-ray diffraction and evolved gas analysis show a strong paleoenvironmental dependency. While perennial lake mudstones are characterized by Fe-saponite, we find that stratigraphic intervals associated with episodic lake drying contain Al-rich, Fe3+-bearing dioctahedral smectite, with minor (3 wt %) quantities of ferripyrophyllite, interpreted as wind-blown detritus, found in candidate aeolian deposits. Our results suggest that dioctahedral smectite formed via near-surface chemical weathering driven by fluctuations in lake level and atmospheric infiltration, a process leading to the redistribution of nutrients and potentially influencing the cycling of gases that help regulate climate.
Figures
References
-
- Grotzinger J. P., Sumner D. Y., Kah L. C., Stack K., Gupta S., Edgar L., Rubin D., Lewis K., Schieber J., Mangold N., Milliken R., Conrad P. G., DesMarais D., Farmer J., Siebach K., Calef F. III, Hurowitz J., McLennan S. M., Ming D., Vaniman D., Crisp J., Vasavada A., Edgett K. S., Malin M., Blake D., Gellert R., Mahaffy P., Wiens R. C., Maurice S., Grant J. A., Wilson S., Anderson R. C., Beegle L., Arvidson R., Hallet B., Sletten R. S., Rice M., Bell J. III, Griffes J., Ehlmann B., Anderson R. B., Bristow T. F., Dietrich W. E., Dromart G., Eigenbrode J., Fraeman A., Hardgrove C., Herkenhoff K., Jandura L., Kocurek G., Lee S., Leshin L. A., Leveille R., Limonadi D., Maki J., McCloskey S., Meyer M., Minitti M., Newsom H., Oehler D., Okon A., Palucis M., Parker T., Rowland S., Schmidt M., Squyres S., Steele A., Stolper E., Summons R., Treiman A., Williams R., Yingst A., MSL Science Team , A habitable fluvio-lacustrine environment at Yellowknife Bay, Gale crater, Mars. Science 343, 1242777 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Grotzinger J. P., Gupta S., Malin M. C., Rubin D. M., Schieber J., Siebach K., Sumner D. Y., Stack K. M., Vasavada A. R., Arvidson R. E., Calef F. III, Edgar L., Fischer W. F., Grant J. A., Griffes J., Kah L. C., Lamb M. P., Lewis K. W., Mangold N., Minitti M. E., Palucis M., Rice M., Williams R. M. E., Yingst R. A., Blake D., Blaney D., Conrad P., Crisp J., Dietrich W. E., Dromart G., Edgett K. S., Ewing R. C., Gellert R., Hurowitz J. A., Kocurek G., Mahaffy P., McBride M. J., McLennan S. M., Mischna M., Ming D., Milliken R., Newsom H., Oehler D., Parker T. J., Vaniman D., Wiens R. C., Wilson S. A., Deposition, exhumation, and paleoclimate of an ancient lake deposit, Gale crater, Mars. Science 350, aac7575 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Vaniman D. T., Bish D. L., Ming D. W., Bristow T. F., Morris R. V., Blake D. F., Chipera S. J., Morrison S. M., Treiman A. H., Rampe E. B., Rice M., Achilles C. N., Grotzinger J. P., McLennan S. M., Williams J., Bell J. F. III, Newsom H. E., Downs R. T., Maurice S., Sarrazin P., Yen A. S., Morookian J. M., Farmer J. D., Stack K., Milliken R. E., Ehlmann B. L., Sumner D. Y., Berger G., Crisp J. A., Hurowitz J. A., Anderson R., Des Marais D. J., Stolper E. M., Edgett K. S., Gupta S., Spanovich N., MSL Science Team , Mineralogy of a mudstone at Yellowknife Bay, Gale crater, Mars. Science 343, 1243480 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Bristow T. F., Bish D. L., Vaniman D. T., Morris R. V., Blake D. F., Grotzinger J. P., Rampe E. B., Crisp J. A., Achilles C. N., Ming D. W., Ehlmann B. L., King P. L., Bridges J. C., Eigenbrode J. L., Sumner D. Y., Chipera S. J., Michael Moorokian J., Treiman A. H., Morrison S. M., Downs R. T., Farmer J. D., Des Marais D., Sarrazin P., Floyd M. M., Mischna M. A., McAdam A. C., The origin and implications of clay minerals from Yellowknife Bay, Gale crater, Mars. Am. Mineral. 100, 824–836 (2015). - PMC - PubMed
-
- McLennan S. M. Anderson R. B., Bell J. F. III, Bridges J. C., Calef F. III, Campbell J. L., Clark B. C., Clegg S., Conrad P., Cousin A., Des Marais D. J., Dromart G., Dyar M. D., Edgar L. A., Ehlmann B. L., Fabre C., Forni O., Gasnault O., Gellert R., Gordon S., Grant J. A., Grotzinger J. P., Gupta S., Herkenhoff K. E., Hurowitz J. A., King P. L., Le Mouélic S., Leshin L. A., Léveillé R., Lewis K. W., Mangold N., Maurice S., Ming D. W., Morris R. V., Nachon M., Newsom H. E., Ollila A. M., Perrett G. M., Rice M. S., Schmidt M. E., Schwenzer S. P., Stack K., Stolper E. M., Sumner D. Y., Treiman A. H., VanBommel S., Vaniman D. T., Vasavada A., Wiens R. C., Yingst R. A., MSL Science Team , Elemental geochemistry of sedimentary rocks at Yellowknife Bay, Gale crater, Mars. Science 343, 1244734 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

