SOXF factors regulate murine satellite cell self-renewal and function through inhibition of β-catenin activity
- PMID: 29882512
- PMCID: PMC6021169
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.26039
SOXF factors regulate murine satellite cell self-renewal and function through inhibition of β-catenin activity
Abstract
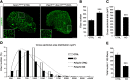
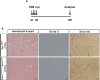
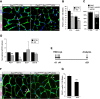
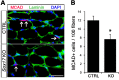
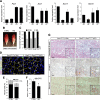
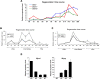
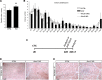
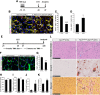
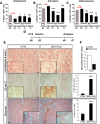
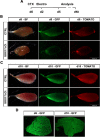
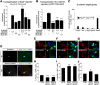
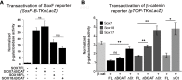
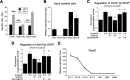
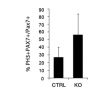
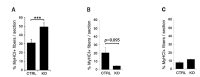
Muscle satellite cells are the primary source of stem cells for postnatal skeletal muscle growth and regeneration. Understanding genetic control of satellite cell formation, maintenance, and acquisition of their stem cell properties is on-going, and we have identified SOXF (SOX7, SOX17, SOX18) transcriptional factors as being induced during satellite cell specification. We demonstrate that SOXF factors regulate satellite cell quiescence, self-renewal and differentiation. Moreover, ablation of Sox17 in the muscle lineage impairs postnatal muscle growth and regeneration. We further determine that activities of SOX7, SOX17 and SOX18 overlap during muscle regeneration, with SOXF transcriptional activity requisite. Finally, we show that SOXF factors also control satellite cell expansion and renewal by directly inhibiting the output of β-catenin activity, including inhibition of Ccnd1 and Axin2. Together, our findings identify a key regulatory function of SoxF genes in muscle stem cells via direct transcriptional control and interaction with canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Keywords: SoxF; adult stem cells; developmental biology; mouse; regenerative medicine; satellite cells; self-renewal; skeletal muscle regeneration; stem cells; ß-catenin.
© 2018, Alonso-Martin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
SA, FA, DM, AR, PZ, FR No competing interests declared
Figures
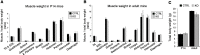
References
-
- Alonso-Martin S, Rochat A, Mademtzoglou D, Morais J, de Reyniès A, Auradé F, Chang TH, Zammit PS, Relaix F. Gene expression profiling of muscle stem cells identifies novel regulators of postnatal myogenesis. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 2016;4:58. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2016.00058. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bernard P, Harley VR. Acquisition of SOX transcription factor specificity through protein-protein interaction, modulation of Wnt signalling and post-translational modification. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology. 2010;42:400–410. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.10.017. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

