Registration of Laser Scanning Point Clouds: A Review
- PMID: 29883397
- PMCID: PMC5981425
- DOI: 10.3390/s18051641
Registration of Laser Scanning Point Clouds: A Review
Abstract
The integration of multi-platform, multi-angle, and multi-temporal LiDAR data has become important for geospatial data applications. This paper presents a comprehensive review of LiDAR data registration in the fields of photogrammetry and remote sensing. At present, a coarse-to-fine registration strategy is commonly used for LiDAR point clouds registration. The coarse registration method is first used to achieve a good initial position, based on which registration is then refined utilizing the fine registration method. According to the coarse-to-fine framework, this paper reviews current registration methods and their methodologies, and identifies important differences between them. The lack of standard data and unified evaluation systems is identified as a factor limiting objective comparison of different methods. The paper also describes the most commonly-used point cloud registration error analysis methods. Finally, avenues for future work on LiDAR data registration in terms of applications, data, and technology are discussed. In particular, there is a need to address registration of multi-angle and multi-scale data from various newly available types of LiDAR hardware, which will play an important role in diverse applications such as forest resource surveys, urban energy use, cultural heritage protection, and unmanned vehicles.
Keywords: coarse-to-fine strategy; laser scanning; point clouds; registration; review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
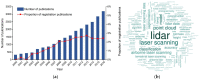
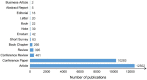
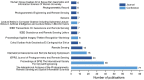
References
-
- Anuta P.E. Spatial registration of multispectral and multitemporal digital imagery using fast Fourier transform techniques. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Electron. 1970;8:353–368. doi: 10.1109/TGE.1970.271435. - DOI
-
- Smith S.M., Brady J.M. SUSAN—A new approach to low level image processing. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1997;23:45–78. doi: 10.1023/A:1007963824710. - DOI
-
- Lowe D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004;60:91–110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94. - DOI
-
- Matas J., Chum O., Urban M., Pajdla T. Robust wide-baseline stereo from maximally stable extremal regions. Image Vis. Comput. 2004;22:761–767. doi: 10.1016/j.imavis.2004.02.006. - DOI
-
- Bay H., Tuytelaars T., Van Gool L. European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2006. Surf: Speeded up robust features; pp. 404–417.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

