A silver lining for 24-hydroxycholesterol in Alzheimer's disease: The involvement of the neuroprotective enzyme sirtuin 1
- PMID: 29883958
- PMCID: PMC6007083
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.05.009
A silver lining for 24-hydroxycholesterol in Alzheimer's disease: The involvement of the neuroprotective enzyme sirtuin 1
Abstract
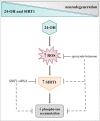
It is now established that cholesterol oxidation products (oxysterols) are involved in several events underlying Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis. Of note, certain oxysterols cause neuron dysfunction and degeneration but, recently, some of them have been shown also to have neuroprotective effects. The present study, which aimed to understand the potential effects of 24-hydroxycholesterol (24-OH) against the intraneuronal accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau protein, stressed these latter effects. A beneficial effect of 24-OH was demonstrated in SK-N-BE neuroblastoma cells, and is due to its ability to modulate the deacetylase sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), which contributes to preventing the neurotoxic accumulation of the hyperphosphorylated tau protein. Unlike 24-OH, 7-ketocholesterol (7-K) did not modulate the SIRT1-dependent neuroprotective pathway. To confirm the neuroprotective role of 24-OH, in vivo experiments were run on mice that express human tau without spontaneously developing tau pathology (hTau mice), by means of the intracerebroventricular injection of 24-OH. 24-OH, unlike 7-K, was found to completely prevent the hyperphosphorylation of tau induced by amyloid β monomers. These data highlight the importance of preventing the loss of 24-OH in the brain, and of maintaining high levels of the enzyme SIRT1, in order to counteract neurodegeneration.
Keywords: 24-hydroxycholesterol; Alzheimer's disease; Oxysterols; Sirtuin 1; Tau.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
24-Hydroxycholesterol Induces Tau Proteasome-Dependent Degradation via the SIRT1/PGC1α/Nrf2 Pathway: A Potential Mechanism to Counteract Alzheimer's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;12(3):631. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030631. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978879 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of CX3CR1 and Fractalkine Chemokines in Amyloid Beta Clearance and p-Tau Accumulation in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) Rodent Models: Is Fractalkine a Systemic Biomarker for AD?Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(4):403-12. doi: 10.2174/1567205013666151116125714. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016. PMID: 26567742 Review.
-
Changes in brain oxysterols at different stages of Alzheimer's disease: Their involvement in neuroinflammation.Redox Biol. 2016 Dec;10:24-33. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2016.09.001. Epub 2016 Sep 16. Redox Biol. 2016. PMID: 27687218 Free PMC article.
-
SLOH, a carbazole-based fluorophore, mitigates neuropathology and behavioral impairment in the triple-transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Neuropharmacology. 2018 Mar 15;131:351-363. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.01.003. Epub 2018 Jan 5. Neuropharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29309769
-
Mouse models of Alzheimer's disease: the long and filamentous road.Neurol Res. 2003 Sep;25(6):590-600. doi: 10.1179/016164103101202020. Neurol Res. 2003. PMID: 14503012 Review.
Cited by
-
The Beneficial Roles of SIRT1 in Neuroinflammation-Related Diseases.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Sep 14;2020:6782872. doi: 10.1155/2020/6782872. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33014276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress and Beta Amyloid in Alzheimer's Disease. Which Comes First: The Chicken or the Egg?Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Sep 16;10(9):1479. doi: 10.3390/antiox10091479. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholesterol Dysmetabolism in Alzheimer's Disease: A Starring Role for Astrocytes?Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Nov 26;10(12):1890. doi: 10.3390/antiox10121890. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of cholesterol metabolism on hepatolithiasis.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Jan 7;31(1):99960. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i1.99960. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 39777239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidized cholesterol species as signaling molecules in the brain: diabetes and Alzheimer's disease.Neuronal Signal. 2019 Dec;3(4):NS20190068. doi: 10.1042/NS20190068. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Neuronal Signal. 2019. PMID: 32269839 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Braak H., Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82:239–259. - PubMed
-
- Braak H., Del Tredici K. The preclinical phase of the pathological process underlying sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Brain. 2015;138:2814–2833. - PubMed
-
- Mattson M.P. Acetylation unleashes protein demons of dementia. Neuron. 2010;67:900–902. - PubMed
-
- Giudetti A.M., Romano A., Lavecchia A.M., Gaetani S. The role of brain cholesterol and its oxidized products in Alzheimer's disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2016;13:198–205. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

